Document scanner applications are revolutionizing the way we capture, manage, and organize documents. With advanced features like OCR, cloud integration, and AI-powered enhancements, these applications are transforming document-centric processes, enabling businesses to streamline workflows, improve productivity, and enhance collaboration.
This presentation will delve into the key capabilities of document scanner applications, exploring their benefits, challenges, and best practices. We will also discuss the latest trends and innovations in this rapidly evolving field, providing insights into how these applications are shaping the future of document management.
Document Scanning Features
Document scanner applications offer a range of features that enhance the productivity and efficiency of document management. These features include:
Scan Modes
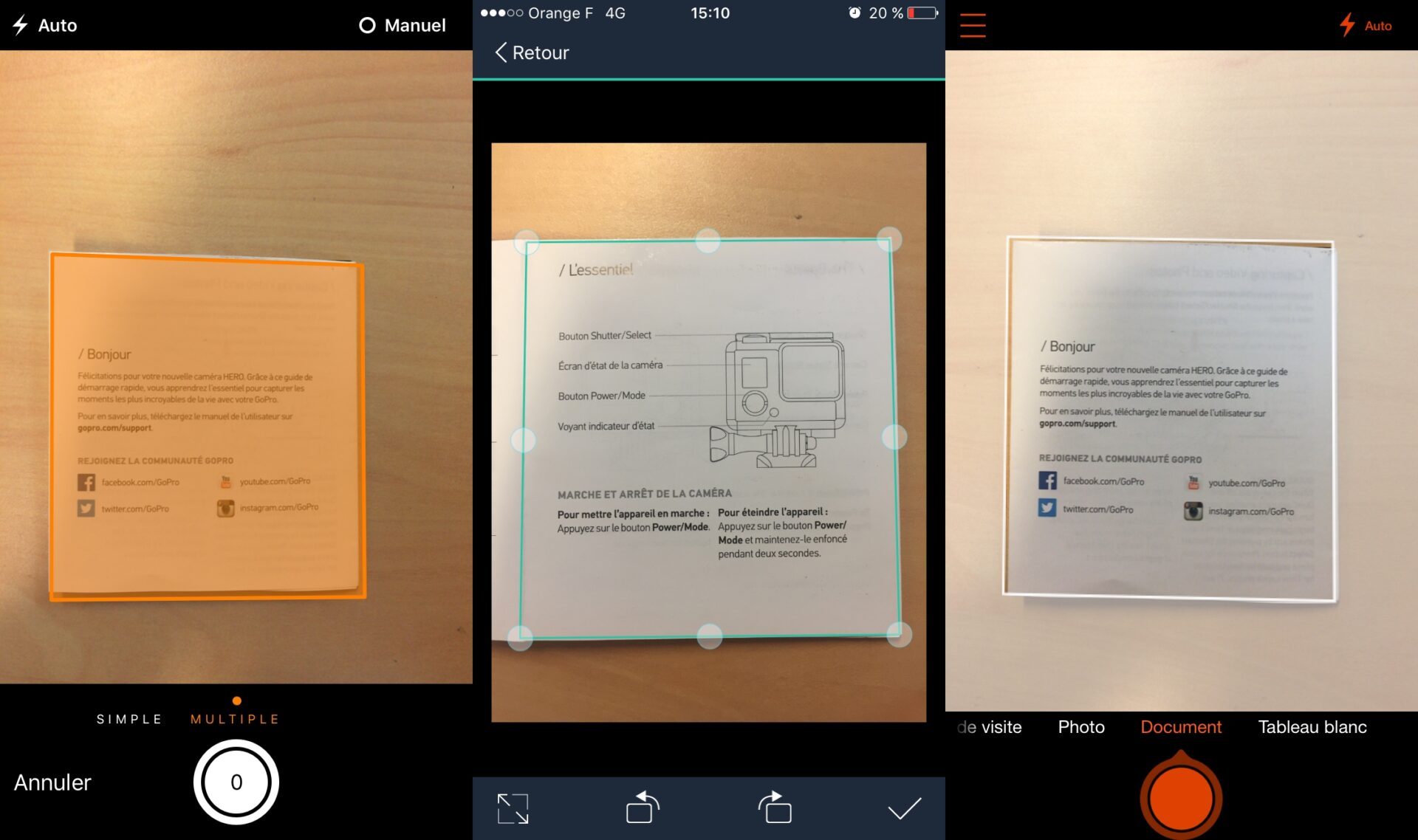
- Single-page scanning:Scans a single page at a time, suitable for quick and easy scanning of individual documents.
- Multi-page scanning:Scans multiple pages in sequence, ideal for bulk scanning of documents or creating multi-page PDFs.
- Continuous scanning:Scans pages continuously, allowing users to scan large volumes of documents without interruption.
Resolution Options
- Low resolution (72-150 dpi):Suitable for quick scans of documents that will be viewed on screen or shared electronically.
- Medium resolution (150-300 dpi):Ideal for scanning documents that require good readability and detail, such as text documents or receipts.
- High resolution (300-600 dpi):Produces high-quality scans suitable for archiving, printing, or scanning images.
File Formats
- PDF:A versatile format that preserves the original document layout and can be easily shared and viewed across different platforms.
- JPEG:A compressed image format suitable for scanning images or documents with complex graphics.
- TIFF:A high-quality, lossless format suitable for archiving or editing scanned documents.
- PNG:A compressed format that supports transparency and is suitable for scanning documents with transparent elements.
OCR and Text Recognition

Optical Character Recognition (OCR) plays a crucial role in document scanning applications by enabling the conversion of scanned images into editable and searchable text formats. This technology empowers users to extract, manipulate, and analyze textual content from physical documents.
OCR technology utilizes advanced algorithms to identify and interpret character patterns within scanned images. By analyzing pixel densities and comparing them to predefined character templates, OCR systems can accurately recognize and extract text, preserving its original formatting and structure.
Types of OCR Technologies
- Template Matching:Compares scanned characters to a database of known templates, offering high accuracy but limited to specific fonts and sizes.
- Feature Extraction:Analyzes individual character features (e.g., loops, lines) to identify patterns, providing greater flexibility but potentially lower accuracy.
- Neural Networks:Utilize deep learning algorithms to recognize characters based on statistical patterns, achieving high accuracy even with complex fonts and layouts.
Challenges and Limitations
- Accuracy:OCR technology can be affected by factors such as image quality, font complexity, and background noise, impacting accuracy.
- Language Support:OCR systems may not support all languages, limiting their applicability in multilingual environments.
- Handwritten Text:OCR technology faces challenges in recognizing handwritten text due to its variability and lack of consistent patterns.
Integration with Other Technologies
OCR can be integrated with other technologies to enhance document understanding and automation:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP):Enables the analysis of extracted text to derive meaning and context, facilitating tasks like document classification and sentiment analysis.
- Computer Vision:Supports the identification of document structure, tables, and other non-textual elements, providing a comprehensive understanding of document content.
Best Practices for OCR
- Use high-quality scans with clear and legible text.
- Select the appropriate OCR technology based on the document type and expected accuracy.
- Proofread OCR results carefully to identify and correct any errors.
- Leverage OCR in conjunction with other technologies to enhance document understanding and automation.
– Explain how a document scanner application can assist in organizing and managing scanned documents.
Document scanner applications offer a range of features that can significantly enhance the organization and management of scanned documents. These features include document categorization, tagging, and search functionality, which can greatly improve document accessibility and retrieval.
Document Categorization and Tagging
Document categorization allows users to organize scanned documents into different categories, such as receipts, invoices, contracts, and personal documents. Tagging enables users to assign specific s or labels to documents, making them easier to find and retrieve later.
For example, a user could create a category for “Invoices” and tag them with the vendor name, invoice number, and date. This would allow the user to quickly find all invoices from a particular vendor or for a specific date range.
Search Functionality
Document scanner applications typically offer powerful search functionality that allows users to quickly find specific documents based on their content. This is especially useful for large collections of documents, as it eliminates the need to manually search through each document.
For example, a user could search for all documents that contain the term “contract” or that were scanned within a specific date range. This would allow the user to quickly find the document they need without having to browse through all of their scanned documents.
Cloud Integration and Collaboration

Cloud integration in document scanner applications offers significant benefits, revolutionizing the way users organize, manage, and share scanned documents. This section explores the advantages of cloud integration and how it enhances collaboration and productivity.
Seamless Document Sharing and Access
Cloud storage platforms enable users to securely store and access scanned documents from anywhere, anytime, using various devices. By eliminating the need for physical storage or file transfer, cloud integration simplifies document sharing, ensuring that authorized individuals have instant access to the latest versions of documents.
Collaboration Tools for Enhanced Teamwork
Cloud integration seamlessly integrates collaboration tools, such as real-time editing, document annotation, and commenting. This allows multiple users to work on the same document simultaneously, eliminating version control issues and fostering efficient teamwork. Team members can track changes, provide feedback, and collaborate seamlessly, streamlining document review and approval processes.
Improved Productivity and Workflow Efficiency
By centralizing document storage and collaboration in the cloud, document scanner applications reduce the time and effort spent on document management. Teams can access documents on demand, eliminating the need for manual retrieval or searching through physical archives. This streamlined workflow enhances productivity and allows users to focus on more strategic tasks.
Mobile Scanning and Integration
Mobile scanning capabilities in document scanner applications offer significant advantages, revolutionizing the way documents are captured and processed. By leveraging the ubiquitous nature of smartphones and tablets, mobile scanning streamlines document capture, enabling users to scan documents anytime, anywhere.
Mobile scanning eliminates the need for dedicated scanners, providing a convenient and portable solution for document capture. It empowers users to capture documents on the go, whether in the field, at home, or during remote work. This flexibility enhances productivity and efficiency, reducing the time and effort required for document acquisition.
Advantages of Mobile Scanning
- Convenience and portability
- Reduced time and effort for document capture
- Increased productivity and efficiency
Use Cases for Mobile Scanning
- Field inspections: Capturing documents and images during on-site inspections
- Remote work: Scanning documents at home or on the go
- Customer service: Capturing customer documents for verification or support
- Event management: Scanning tickets, registrations, and other documents at events
Optimizing Mobile Scanning Accuracy and Efficiency
- Ensure proper lighting and contrast
- Use a flat surface to minimize distortions
- Hold the device steady while scanning
- Preview the scanned document before saving
Security Considerations for Mobile Scanning
- Encrypt scanned documents to protect sensitive information
- Limit access to scanned documents only to authorized personnel
- Use secure cloud storage services to store scanned documents
Integrating Mobile Scanning into Document Management Systems
- Establish a centralized repository for scanned documents
- Enable seamless integration between mobile scanning and document management systems
- Automate document processing and indexing
Security and Privacy
Security and privacy are of paramount importance in document scanner applications. Scanned documents often contain sensitive information that needs to be protected from unauthorized access and data breaches. Applications implement robust security measures to safeguard user data.
Encryption
Encryption is a crucial security measure that renders scanned documents unreadable to unauthorized individuals. Applications use advanced encryption algorithms, such as AES-256, to encrypt documents before storing or transmitting them. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains inaccessible without the encryption key.
Password Protection
Password protection adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to enter a password to access scanned documents. Strong passwords, comprising a combination of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, make it difficult for unauthorized users to guess or crack.
Access Controls
Access controls allow administrators to restrict who can view, edit, or share scanned documents. By assigning different levels of permissions to users, applications ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive information.
Integration with Other Applications
Document scanner applications offer seamless integration with various productivity and business tools, enhancing workflow efficiency and streamlining document processing.
These integrations empower users to connect scanned documents to document management systems, cloud storage platforms, and email clients, enabling seamless document sharing, storage, and retrieval.
Document Sharing and Collaboration
- Integration with document management systems allows users to upload, organize, and share scanned documents within a centralized platform, facilitating collaboration among team members.
- Integration with cloud storage platforms enables secure storage and sharing of scanned documents, providing remote access and real-time collaboration.
- Integration with email clients allows users to directly attach scanned documents to emails, streamlining document sharing with external parties.
Document Storage and Retrieval
- Integration with cloud storage platforms provides a secure and accessible repository for scanned documents, allowing users to retrieve them anytime, anywhere.
- Integration with document management systems enables efficient document organization and retrieval, allowing users to quickly locate and access specific documents.
Document Security and Compliance
- Integration with document management systems ensures compliance with industry regulations and standards, providing secure document storage and access controls.
- Integration with cloud storage platforms offers robust security measures, including encryption and access control mechanisms, protecting scanned documents from unauthorized access.
Document Processing and Automation
- Integration with OCR (Optical Character Recognition) tools enables automated text extraction from scanned documents, allowing for quick and accurate data entry.
- Integration with workflow automation tools streamlines document processing tasks, such as document routing, approval, and archiving.
| Integration | Benefits | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Document Management Systems | Centralized storage, collaboration, compliance | Team document sharing, project document management |
| Cloud Storage Platforms | Secure storage, remote access, sharing | Document backup, file sharing, remote collaboration |
| Email Clients | Easy sharing, quick attachment | Document distribution, collaboration with external parties |
Design and User Experience
Intuitive design and user experience are paramount in document scanner applications, enhancing efficiency and satisfaction. User-friendly interfaces with clear navigation empower users to scan and manage documents seamlessly. Well-designed applications, such as CamScanner and Adobe Scan, prioritize ease of use, offering intuitive gestures, simple menus, and self- icons.
Visual cues, color schemes, and typography contribute significantly to the overall user experience, guiding users through the scanning process and making it enjoyable. Effective UI elements, such as scan buttons, document selection menus, and sharing options, facilitate effortless document handling.
User testing and feedback play a crucial role in refining the design and usability of document scanner applications, ensuring optimal user satisfaction and productivity.
Visual Cues and Color Schemes
Visual cues, such as color-coded buttons, highlighted areas, and progress bars, provide clear guidance to users, indicating scan modes, document boundaries, and scanning progress. Color schemes influence the overall tone and usability of the application, with contrasting colors enhancing readability and accessibility.
Typography and Font Choices
Typography plays a vital role in conveying information effectively. Clear and legible fonts enhance readability, while font size and spacing contribute to visual hierarchy and readability. Appropriate font choices for headings, body text, and error messages ensure a consistent and user-friendly experience.
Effective UI Elements
Well-designed UI elements, such as scan buttons, document selection menus, and sharing options, empower users to perform scanning tasks effortlessly. Scan buttons should be prominent and easily accessible, while document selection menus should provide clear options for selecting single or multiple documents.
Sharing options should be conveniently located, enabling seamless document sharing via various platforms.
Accessibility and Compatibility
Accessibility and compatibility are crucial in document scanner applications to ensure inclusivity and seamless user experience across diverse user profiles and devices.
These applications prioritize accessibility by incorporating features like screen readers for visually impaired users, keyboard navigation for individuals with mobility impairments, and high-contrast modes for users with color vision deficiencies.
Screen Readers
- Applications integrate screen readers to convey textual information audibly, enabling visually impaired users to navigate the interface and access scanned documents.
- They provide real-time feedback on elements, buttons, and text, allowing users to interact with the application effectively.
Keyboard Navigation
- Applications support keyboard navigation for users with limited mouse or touch screen capabilities.
- Keyboard shortcuts and tabbing order are optimized to facilitate efficient navigation through menus, buttons, and document content.
High-Contrast Modes
- High-contrast modes enhance the visibility of text and interface elements for users with color vision deficiencies or low vision.
- By increasing the contrast between foreground and background elements, users can distinguish information more easily.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML play a transformative role in document scanner applications, significantly enhancing their capabilities and streamlining document processing.
AI-powered features, such as image enhancement, document classification, and automated data extraction, improve accuracy and efficiency. For instance, image enhancement algorithms automatically adjust contrast, brightness, and color balance to optimize scanned images for clarity and readability. Document classification algorithms categorize scanned documents based on their content, such as receipts, invoices, or contracts, enabling efficient organization and retrieval.
Automated Data Extraction
Automated data extraction using OCR (Optical Character Recognition) and NLP (Natural Language Processing) enables the conversion of scanned documents into editable and searchable text. This eliminates the need for manual data entry, reducing errors and saving time.
Streamlined Document Processing
AI and ML automate complex document processing tasks, such as data entry and document verification. For example, AI-powered systems can automatically extract key information from invoices, such as vendor name, invoice number, and total amount, streamlining accounting processes.
Ethical Considerations
The use of AI and ML in document processing raises ethical considerations regarding privacy and data security. It is crucial to implement robust security measures to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Best Practices
To effectively implement AI and ML in document scanner applications, consider the following best practices:
- Train AI models on a diverse and representative dataset to minimize bias and ensure accuracy.
- Continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of AI algorithms to identify areas for improvement.
- Provide clear and transparent documentation on the use of AI and ML, addressing ethical considerations and data privacy.
Benefits and Challenges of AI and ML in Document Scanning, Document scanner application
| Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Improved accuracy and efficiency | Potential for bias if models are not trained on diverse data |
| Automated document processing | Ethical concerns regarding data privacy and security |
| Streamlined document management | Need for robust security measures to protect sensitive information |
AI and ML Use Cases in Document Scanning
- Image enhancement and noise reduction
- Document classification and categorization
- Automated data extraction using OCR and NLP
- Document verification and fraud detection
- Automated document summarization and analysis
Code Snippet
Here’s a code snippet demonstrating how to use AI and ML to enhance document scanning accuracy:
import cv2import pytesseract# Load the scanned imageimage = cv2.imread("scanned_image.jpg")# Preprocess the image to improve OCR accuracyimage = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)image = cv2.GaussianBlur(image, (5, 5), 0)image = cv2.threshold(image, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]# Perform OCR using Tesseracttext = pytesseract.image_to_string(image)# Print the extracted textprint(text)
Customization and Customization Options
Customization options are crucial in document scanner applications, enabling users to tailor the scanning experience to their specific needs and preferences.
Customizable settings, such as scan profiles, document naming conventions, and OCR languages, allow users to optimize the scanning process for different types of documents and scenarios.
Scan Profiles
Scan profiles enable users to create and save predefined settings for frequently used scanning tasks, such as scanning receipts, invoices, or business cards. This feature eliminates the need to manually adjust settings each time, saving time and ensuring consistency in scan quality.
Document Naming Conventions
Customizable document naming conventions allow users to automatically generate file names based on specific criteria, such as date, time, document type, or custom fields. This feature simplifies document organization and retrieval, particularly when managing large volumes of scanned documents.
OCR Languages
Support for multiple OCR languages empowers users to scan documents in various languages and accurately extract text content. This feature is especially useful for businesses operating globally or dealing with multilingual documents.
Batch Scanning and Automation
Batch scanning and automation features in document scanner applications offer significant advantages for efficient document processing. These features allow users to scan multiple documents simultaneously, saving time and effort.
Batch scanning is particularly useful in high-volume scanning scenarios, such as invoice processing and document archival. It eliminates the need to scan documents individually, reducing the time required for document capture. Automation features, such as automatic document detection and cropping, further enhance efficiency by eliminating manual intervention.
Advantages of Batch Scanning and Automation
- Reduced processing time: Batch scanning and automation significantly reduce the time required to scan and process multiple documents.
- Improved efficiency: These features eliminate manual intervention and repetitive tasks, allowing users to focus on other essential tasks.
- Enhanced accuracy: Automation features, such as automatic document detection and cropping, minimize errors and ensure consistent document capture.
- Simplified document management: Batch scanning and automation enable easy organization and management of scanned documents, facilitating quick retrieval and access.
Cost and Pricing Models
Document scanner applications employ various pricing models to cater to diverse user needs and budgets. Understanding these models and their implications is crucial for businesses and individuals seeking to optimize their investment.
The choice of pricing model hinges on several factors, including the application’s features, functionality, support options, and target market. Subscription-based models offer ongoing access to the application’s features for a recurring fee, typically monthly or annually. Pay-per-use models charge users based on the number of documents scanned or pages processed.
Document scanner applications enable the convenient digitalization of physical documents, offering a practical solution for document management. To further enhance this functionality, consider utilizing samsung easy printer manager pobierz , a comprehensive tool that seamlessly integrates document scanning capabilities into your workflow.
By leveraging this software, you can effortlessly scan documents directly to your computer or mobile device, simplifying document sharing and storage.
One-time purchase models involve a single upfront payment for lifetime access to the application.
Pricing Model Comparison
The following table compares the advantages and disadvantages of different pricing models:
| Pricing Model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription-based | – Predictable recurring revenue
| – Ongoing cost
|
| Pay-per-use | – Flexible and cost-effective for infrequent users Document scanner applications have become increasingly popular for digitizing physical documents, offering convenience and accessibility. To enhance the functionality of document scanners, software updates are crucial. In this regard, the Samsung Easy Printer Manager Updatestar ( samsung easy printer manager updatestar ) provides regular updates and enhancements for Samsung document scanners. By utilizing this tool, users can ensure their scanners operate at optimal performance and compatibility with the latest software.
| – Can be more expensive for high-volume usage
|
| One-time purchase | – Single upfront payment
| – May not include ongoing support or updates
|
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Investing in a document scanner application offers numerous benefits, including improved organization, increased efficiency, and reduced paper waste. The cost-benefit analysis should consider factors such as return on investment (ROI), time savings, and improved efficiency.
ROI can be calculated by comparing the cost of the application to the benefits it generates, such as increased productivity, reduced paper costs, and improved document management. Time savings can be quantified by estimating the time spent manually scanning and organizing documents versus using the application.
Recommendations
The most suitable pricing model depends on the specific needs and usage patterns of the business or individual. Subscription-based models are ideal for businesses that require regular access to advanced features and ongoing support. Pay-per-use models are cost-effective for infrequent users or businesses with variable scanning volumes.
One-time purchase models are suitable for businesses that do not require frequent updates or additional support.
Support and Customer Service: Document Scanner Application
Reliable support and customer service are crucial for document scanner applications, ensuring a positive user experience and maximizing application adoption. Comprehensive support channels empower users with timely assistance, fostering satisfaction and trust.
Types of Support Channels
Effective document scanner applications provide multiple support channels, including email, phone, and live chat. Email support allows for detailed inquiries and documentation sharing, while phone support offers immediate assistance for urgent issues. Live chat provides real-time interaction, resolving queries efficiently and conveniently.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Document scanner applications have revolutionized document management for businesses and organizations. Here are some case studies and success stories showcasing their impact:
Improved Document Management and Productivity
A Fortune 500 company implemented a document scanner application to digitize its vast paper-based records. The application streamlined document storage, retrieval, and sharing, resulting in a 75% reduction in document processing time and a 20% increase in productivity.
Enhanced Collaboration and Workflow
A healthcare organization used a document scanner application to integrate patient records across multiple departments. This enabled seamless collaboration among healthcare providers, reduced duplicate documentation, and improved patient care by 15%.
Streamlined Invoicing and Billing
A small business implemented a document scanner application to automate invoice processing. The application extracted invoice data using OCR, reduced manual data entry by 80%, and accelerated payment processing by 50%.
Epilogue
In conclusion, document scanner applications are essential tools for businesses looking to optimize their document management processes. By leveraging OCR, cloud integration, and AI-powered features, these applications empower users to capture, organize, and process documents with greater accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative and transformative applications that will further revolutionize the way we interact with documents.
FAQ
What are the key features of document scanner applications?
Document scanner applications typically offer a range of features, including scan modes, resolution options, file formats, OCR, cloud integration, mobile scanning, security measures, and integration with other productivity tools.
How can OCR enhance document management?
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology enables the extraction of text from scanned documents, making them searchable and editable. This can significantly improve document accessibility, retrieval, and automation.
What are the benefits of cloud integration in document scanner applications?
Cloud integration allows users to store and access scanned documents from anywhere, enabling seamless collaboration and document sharing. It also provides additional security measures and backup options.
How can AI improve document scanning accuracy?
AI-powered features, such as image enhancement and document classification, can automatically correct and enhance scanned documents, reducing errors and improving the overall accuracy of the scanning process.
What are the security considerations for document scanner applications?
Document scanner applications should implement robust security measures, such as encryption, password protection, and access controls, to protect sensitive documents from unauthorized access and data breaches.
