What are rafts in 3D printing? In the world of 3D printing, rafts are a crucial support system that helps create stronger and more successful prints, particularly for materials prone to warping or adhesion issues. Think of them as a foundation for your 3D printed creations, ensuring a stable and smooth base for your project.
Rafts are thin layers of material printed directly on the build plate before the actual print begins. They provide a larger surface area for the first layer of your print to adhere to, minimizing the risk of warping and ensuring a solid foundation.
This is particularly important for materials like ABS, PLA, and Nylon, which can be prone to warping and adhesion issues due to their properties.
Introduction to Rafts in 3D Printing
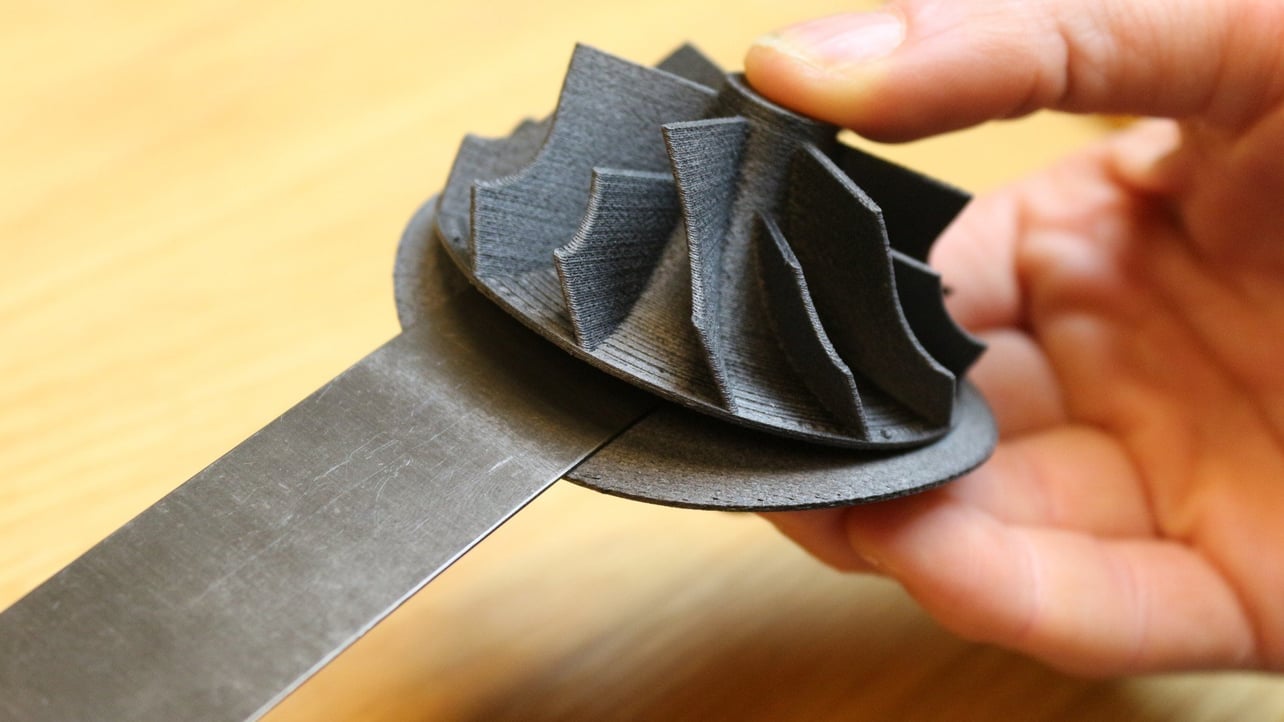
Rafts are a common support structure used in 3D printing to improve the adhesion of the first layer of the print to the print bed. This is particularly important for materials that tend to warp or have poor adhesion to the print bed.
Rafts are typically printed as a thin, flat layer of material that surrounds the base of the print object. They act as a sacrificial layer, providing a larger surface area for the first layer to adhere to and preventing the print from warping.
Common Problems Rafts Address
Rafts are often used to address issues with adhesion and warping during 3D printing.
- Adhesion Issues:Some materials, like ABS and PLA, can have difficulty sticking to the print bed, especially if the bed is not properly leveled. This can lead to the print lifting off the bed during printing, resulting in a failed print.
Rafts provide a larger surface area for the first layer to adhere to, increasing the chances of successful adhesion.
- Warping:Warping is a common problem in 3D printing, particularly with larger prints or materials that are prone to thermal expansion. When a print cools down, the material can contract, causing the print to warp or detach from the print bed.
Rafts help to prevent warping by providing a stable base for the print to adhere to.
Materials That Benefit from Rafts
Rafts are particularly beneficial for materials that have a tendency to warp or have poor adhesion to the print bed. These materials include:
- ABS:ABS is a common 3D printing material known for its strength and durability. However, it can be prone to warping due to its high thermal expansion coefficient. Rafts can help to minimize warping by providing a stable base for the print to adhere to.
- PLA:PLA is another popular 3D printing material known for its ease of use and biodegradability. However, PLA can also be prone to warping, especially when printing large objects. Rafts can help to prevent warping by providing a stable base for the print to adhere to.
- PETG:PETG is a strong and flexible material that is often used for food containers and other applications. However, PETG can also be prone to warping due to its high thermal expansion coefficient. Rafts can help to minimize warping by providing a stable base for the print to adhere to.
How Rafts Work: What Are Rafts In 3d Printing

Rafts are a crucial element in 3D printing, particularly for models with intricate details or large surface areas. They provide a stable foundation for the first layer of your print, ensuring adhesion to the print bed and preventing warping or detaching during the printing process.Rafts are created by extruding a layer of support material onto the print bed before the actual model is printed.
This layer acts as a base for the first layer of the model, ensuring a strong bond and minimizing the risk of adhesion issues. The raft material is usually the same as the material used for the model, but it can be adjusted in terms of thickness and infill density to suit the specific needs of the print.
Relationship Between Raft Thickness and Print Quality
The thickness of the raft plays a significant role in the quality of the final print. A thicker raft provides a more robust base for the model, reducing the risk of warping or detachment. However, an excessively thick raft can lead to excessive material consumption and may make it difficult to remove the finished print from the bed.Here are some general guidelines for choosing the appropriate raft thickness:* Thin rafts (0.5-1.0 mm):Suitable for small models with simple geometries and low risk of warping.
Medium rafts (1.0-2.0 mm)
Ideal for most models with moderate complexity and risk of warping.
Thick rafts (2.0-3.0 mm)
Recommended for large models with intricate details or high risk of warping.
Types of Rafts
D printing software offers various types of rafts, each with its unique characteristics and advantages.
* Standard Raft:The most common type of raft, consisting of a solid layer of material with a uniform thickness.
Sparse Raft
This raft type features a less dense structure, with gaps between the support lines. This reduces material consumption and simplifies removal of the finished print.
Honeycomb Raft
This type of raft has a honeycomb-like structure, offering good adhesion and strength while minimizing material usage.
Advantages of Using Rafts
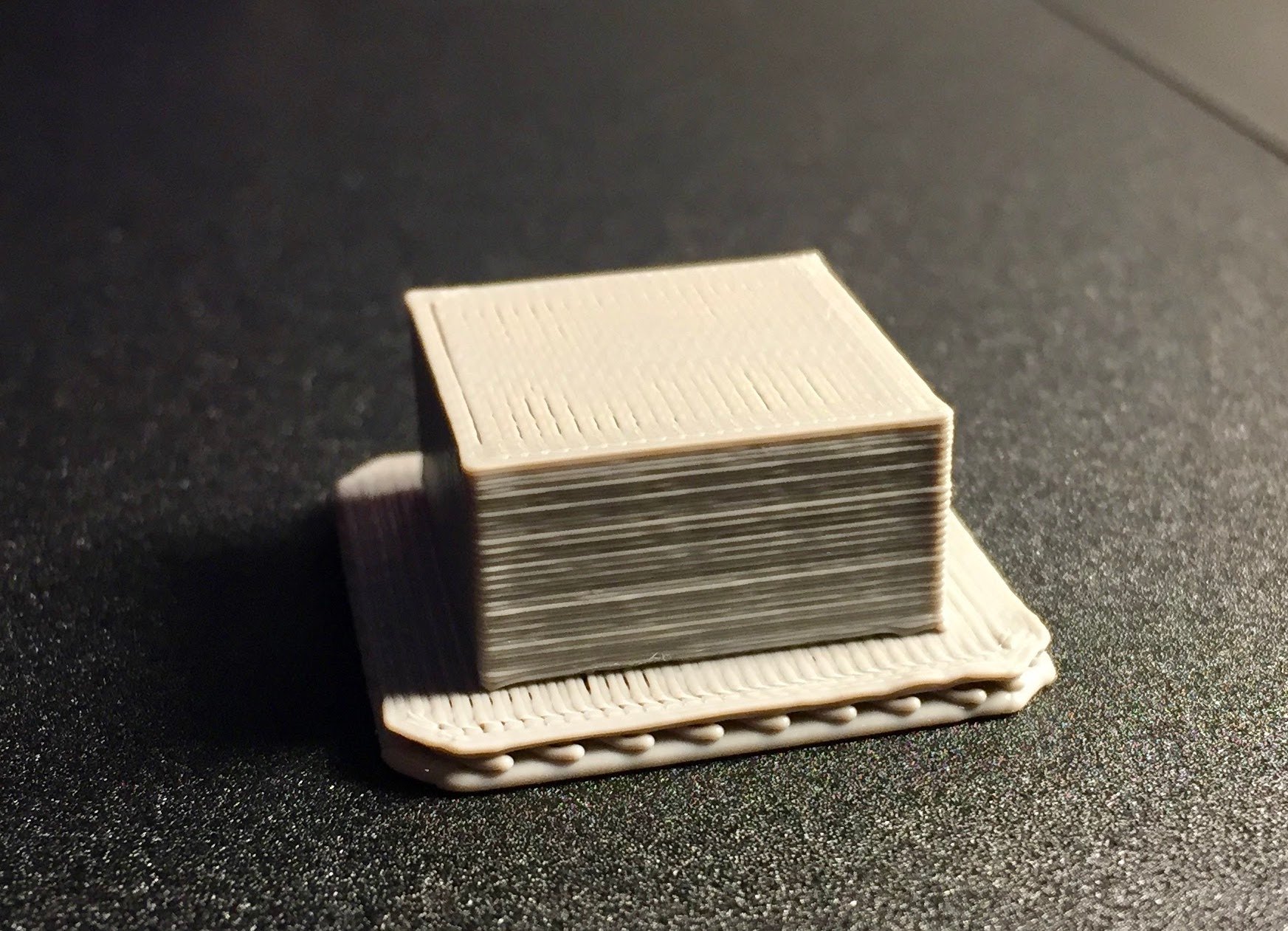
Rafts offer a variety of benefits in 3D printing, particularly for improving print quality and overcoming challenges associated with adhesion and stability.
Improved Adhesion and Stability
Rafts provide a larger surface area for the first layer of your print to adhere to, significantly improving adhesion. This is crucial, especially for prints with intricate details or delicate features. The larger surface area of the raft distributes the weight of the print more evenly, minimizing the risk of the print detaching from the build plate during printing.
Minimizing Warping and Curling
Warpage and curling are common problems in 3D printing, especially with large prints or those made with materials prone to thermal expansion. Rafts help prevent these issues by acting as a heat sink, absorbing some of the heat generated during the printing process.
Imagine a raft in 3D printing as a temporary base for your print, especially useful when your design is small or has a delicate base. It’s like giving your print a stable platform to sit on, helping it stick to the print bed and preventing warping.
This is kind of like how you might collate a document, ensuring everything is in the right order and ready for use. What does it mean to collate on a printer ? Think of it as the print bed organizing the layers of your 3D print, making sure everything sticks together as it should.
Rafts can be removed after printing, leaving you with a clean, finished product.
This helps to maintain a more consistent temperature throughout the print, reducing the likelihood of warping and curling.
Smoother Bottom Surfaces
Prints with intricate details or complex geometries often have uneven or rough bottom surfaces due to the initial layer adhering directly to the build plate. Rafts act as a sacrificial layer, providing a smooth surface for the first layer to adhere to.
This results in a smoother bottom surface for your print, eliminating the need for post-processing to remove imperfections.
Disadvantages of Using Rafts
Rafts, while offering numerous benefits, come with their own set of drawbacks. Understanding these downsides is crucial for making informed decisions about when and whether to use rafts for your 3D prints.
Increased Printing Time
Using rafts adds to the overall printing time. This is because the printer needs to spend additional time laying down the raft material before starting the actual print. The time taken for the raft to be printed depends on its size and the printing speed.
The added time can be significant for larger prints, especially if the raft is thick.
Potential for Raft Removal to Damage Prints
The process of removing the raft from the printed model can be tricky, especially for delicate prints. The raft is often firmly attached to the model, and forceful removal can lead to damage, such as scratches, dents, or even breakage.
This is particularly true for prints with intricate details or fragile structures.
Added Material Cost
Rafts require extra filament, leading to increased material costs. The amount of material used for the raft depends on its size and thickness. This added expense might be significant for large projects or prints requiring multiple rafts.
Alternatives to Rafts
Rafts are a popular solution for improving adhesion in 3D printing, but they aren’t the only option. There are several other techniques and approaches you can use to achieve strong adhesion and prevent warping. Let’s explore some of the alternatives to rafts.
Brim and Skirt
Brim and skirt are two common alternatives to rafts. Both are thin, single-layer structures that are printed around the base of your model. They act as a barrier to prevent the model from lifting during the printing process.A brim is a solid, continuous layer that extends slightly beyond the model’s base.
A skirt, on the other hand, is a series of concentric circles that are printed around the model’s base.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Brim:A brim is more likely to provide better adhesion than a skirt because it is a continuous layer of material. However, it can sometimes leave a small, visible lip around the base of your model.
- Skirt:A skirt is less likely to leave a visible mark on your model because it is a series of separate circles. However, it is less effective at preventing warping than a brim.
Build Plates with Different Surface Textures, What are rafts in 3d printing
The surface of your build plate can significantly impact adhesion. Manufacturers offer various build plate surfaces, each designed to improve adhesion with specific materials.
Build Plate Surface Textures
- Textured Surfaces:Textured surfaces, like those found on glass plates or PEI sheets, offer greater adhesion by providing more surface area for the first layer to bond with.
- Smooth Surfaces:Smooth surfaces, like those found on some FDM printers, are generally less effective at providing adhesion. However, they can be beneficial for certain materials or applications where a smooth finish is desired.
Optimizing Print Settings
Optimizing your print settings can significantly reduce the need for rafts. Here are some tips for improving adhesion and reducing warping:
- Increase Bed Temperature:Increasing the temperature of your build plate can improve adhesion, especially for materials that are prone to warping.
- Adjust Flow Rate:Adjusting the flow rate can impact the thickness of the first layer, which can influence adhesion.
- Use a Heated Enclosure:A heated enclosure can help to maintain a consistent temperature throughout the print, reducing warping and improving adhesion.
- Slow Down Print Speed:Slower print speeds can allow the filament to cool and solidify properly, improving adhesion.
Choosing the Right Raft for Your Print
Choosing the right raft for your print is crucial for a successful 3D printing experience. Rafts are designed to improve adhesion between the print and the build plate, especially for materials prone to warping or sticking. However, different raft types offer varying levels of support and can impact the final print quality.
Understanding the different types and their applications will help you choose the best raft for your specific needs.
Types of Rafts
The choice of raft type depends on the print material, size, and complexity of the design. Here’s a table comparing common raft types and their applications:
| Raft Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Raft | A solid layer of material that provides a large surface area for the print to adhere to. | Suitable for most prints, especially those with large flat surfaces or complex geometries. |
| Sparse Raft | A raft with a grid-like structure, allowing for better airflow and reducing the amount of material used. | Ideal for prints with intricate details or delicate features that might be damaged by a solid raft. |
| Brim Raft | A thin layer of material that extends beyond the perimeter of the print, creating a wider base for better adhesion. | Effective for prints with small base areas or those prone to warping. |
| Support Raft | A combination of a raft and support structures, providing both adhesion and support for overhangs and complex geometries. | Suitable for prints with intricate details, overhangs, or complex shapes. |
Raft Thickness
The thickness of the raft should be adjusted based on the print material and size.
A thicker raft is generally better for larger prints and materials prone to warping, while a thinner raft can be sufficient for smaller prints and materials with good adhesion properties.
Here are some guidelines for raft thickness:* PLA:0.2-0.4mm for small prints, 0.4-0.6mm for larger prints.
ABS
0.4-0.6mm for small prints, 0.6-0.8mm for larger prints.
PETG
0.4-0.6mm for small prints, 0.6-0.8mm for larger prints.
Nylon
0.6-0.8mm for small prints, 0.8-1.0mm for larger prints.
Testing Raft Configurations
The best raft configuration for your print can vary depending on your specific printer, filament, and print settings. It’s important to test different raft types, thicknesses, and infill patterns to find the optimal configuration for your needs.
Experiment with different settings and observe the results. Analyze the adhesion, print quality, and ease of removal to determine the best raft configuration for your specific project.
Removing Rafts from Prints
The raft is designed to provide a stable base for your print, but it needs to be removed after the printing process is complete. Removing the raft without damaging your print requires a careful and methodical approach. This section will guide you through the process of removing rafts from your prints while preserving the integrity of your creation.
Removing Rafts from Prints
Raft removal is a crucial step in 3D printing, and it involves detaching the raft from the printed object without causing any damage. The method of removal depends on the material used for printing and the type of raft employed.
For most prints, a gentle approach is sufficient.
- Inspect the Raft and Print:Begin by carefully examining the raft and the printed object to identify any areas where they are attached. Look for any weak points or areas where the raft might be easily separated.
- Use a Sharp Tool:A sharp tool, such as a hobby knife or a scraper, is useful for gently separating the raft from the print. Apply pressure carefully, ensuring that you are not applying force directly to the print. A gentle rocking motion can be effective in loosening the raft.
- Utilize a Raft Removal Tool:Some 3D printers come equipped with dedicated raft removal tools, which are designed to safely and efficiently detach rafts from prints. These tools often feature a flat blade with a rounded edge, minimizing the risk of scratching the print surface.
- Apply Heat:In some cases, applying heat to the raft can help loosen its adhesion to the print. A hairdryer can be used to gently warm the raft, making it easier to remove. Be cautious not to overheat the print, as this could warp or damage it.
- Soak in Water:For water-soluble support materials, soaking the print in water can dissolve the raft, leaving the printed object intact. This method is particularly effective for prints made with PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) support material.
Cleaning and Smoothing the Print
After removing the raft, it is essential to clean and smooth the print to achieve a professional finish.
- Remove Residual Raft Material:Once the raft is removed, inspect the print for any remaining raft material. Use a soft brush, a damp cloth, or a scraper to gently remove any residue.
- Sanding and Polishing:For prints that require a smooth finish, sanding and polishing can be employed. Start with a coarse-grit sandpaper and gradually move to finer grits to achieve the desired level of smoothness. Be careful not to apply too much pressure, as this could damage the print.
- Acetone Smoothing:For ABS plastic prints, acetone smoothing can be used to remove layer lines and imperfections. Dip a cotton swab in acetone and gently rub it over the print surface. Be cautious not to soak the print in acetone, as this could cause it to warp or dissolve.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the different types of rafts available?
There are various raft types available in 3D printing software, including solid rafts, honeycomb rafts, and sparse rafts. Each type offers different levels of support and can be chosen based on the specific needs of your print.
How do I know if my print needs a raft?
If you’re experiencing issues with warping, adhesion, or a rough bottom surface, a raft can be a good solution. Experiment with different print settings and adhesion solutions to find the best approach for your specific project.
What are some alternatives to using rafts?
Other adhesion solutions include brims, skirts, and textured build plates. These alternatives offer different levels of support and can be chosen based on the complexity and material of your print.
How do I remove a raft from my print?
Carefully pry the raft away from the print using a sharp tool or a pair of tweezers. Be gentle to avoid damaging the print. Once removed, you can clean and smooth the bottom surface using a scraper or sandpaper.
