What does collated mean in printing? Imagine you’re putting together a magazine. You need to make sure the pages are in the correct order, right? Collation is that process of organizing printed pages so they’re ready for binding.
It’s a crucial step in the printing process, ensuring that your final product is complete and error-free.
In the world of printing, collation is more than just arranging pages. It involves understanding different methods, considering the impact on binding, and even exploring how digital printing has changed the process. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of collation and see how it impacts the printed materials we encounter every day.
Collation in Printing
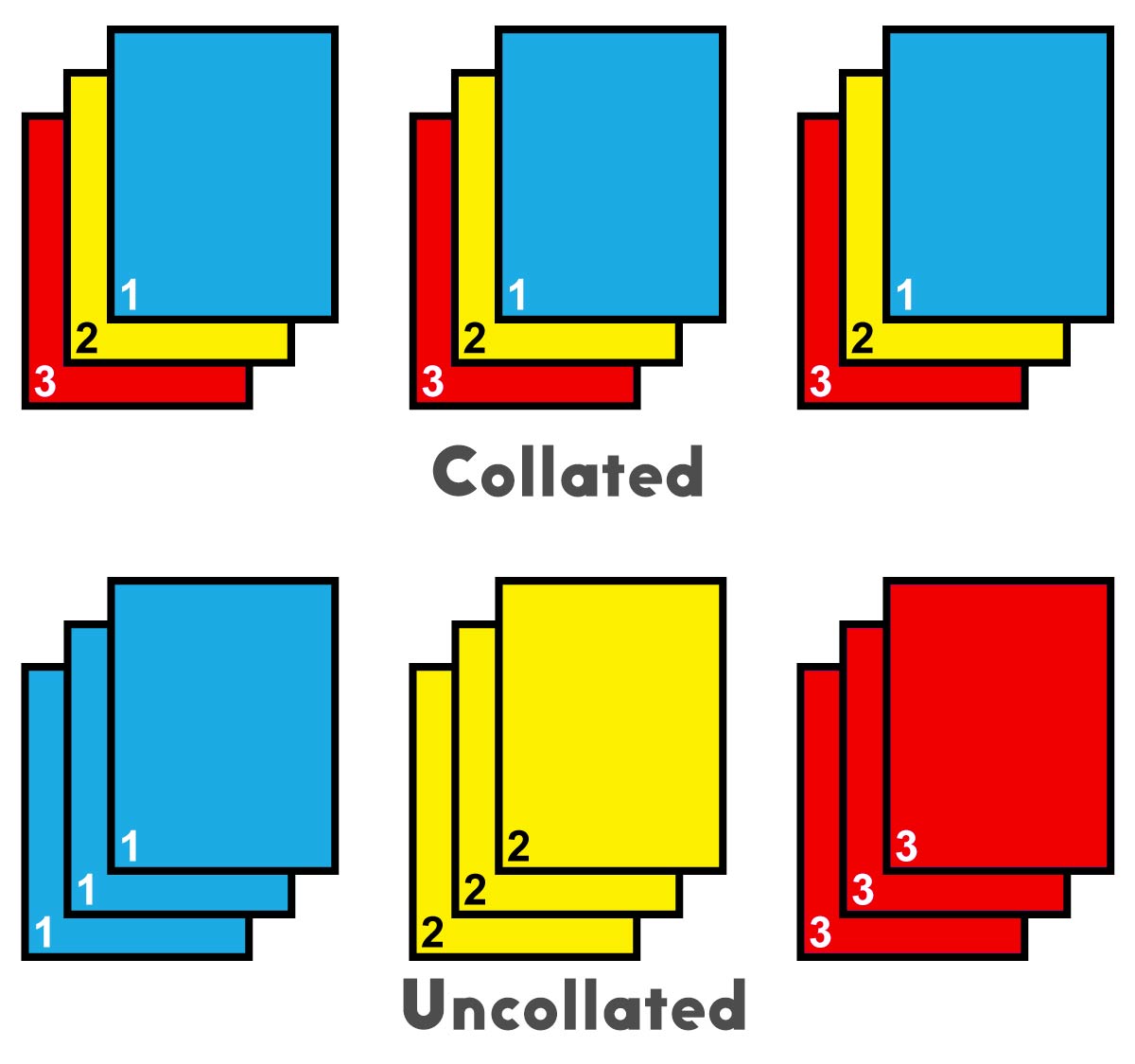
Collation in printing refers to the process of arranging printed pages in the correct order before they are bound or assembled into a final product. Think of it like putting together a puzzle, where each page is a piece that needs to be placed in the right spot to form a complete picture.
Understanding Collation
Collation ensures that the printed pages are in the correct sequence, allowing readers to follow the intended flow of information. Imagine a book where the pages are randomly scattered; it would be impossible to read the story! Collation prevents this by organizing the pages in the order they should appear, making the final printed product readable and user-friendly.
An Example of Collation in Printing, What does collated mean in printing
Let’s say you’re printing a 20-page brochure. Collation ensures that page 1 is followed by page 2, then page 3, and so on, until you reach page 20. This organized arrangement ensures that the brochure’s content is presented in the correct order, allowing readers to understand the information seamlessly.
The Importance of Collation in Printing: What Does Collated Mean In Printing

Collation in printing is a crucial step that ensures the pages of a printed document are assembled in the correct order. It might seem like a simple task, but proper collation is essential for producing high-quality and error-free printed materials.
Benefits of Proper Collation
Proper collation brings several advantages to printing projects. It ensures that the final printed product is accurate, consistent, and professional. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Accurate Page Sequencing:Proper collation guarantees that pages are assembled in the correct order, preventing any skipped or misplaced pages. This ensures a smooth and logical reading experience for the recipient.
- Professional Presentation:A well-collated document reflects professionalism and attention to detail. It shows that the project has been carefully handled, leaving a positive impression on the recipient.
- Reduced Errors and Rework:Accurate collation minimizes the risk of errors like missing pages or incorrect page order. This saves time and resources by eliminating the need for reprinting or correcting mistakes.
- Improved Efficiency:When pages are correctly collated, the finishing process becomes more efficient. This allows for faster production times and reduces delays in delivering the final product.
Impact of Improper Collation
While proper collation brings numerous benefits, improper collation can lead to various issues that negatively impact the final printed product.
So, “collated” in printing basically means that your pages are stacked in the right order, like a proper book. It’s super handy for big projects or reports. Now, if you’re thinking about printing a whole bunch of stuff, you might be wondering how much to print at the library.
Just remember, collated or not, printing costs can add up, so check out those prices before you go wild!
- Disrupted Reading Experience:Incorrectly collated documents can create a confusing and frustrating reading experience. Readers may struggle to follow the flow of information due to misplaced or missing pages.
- Professionalism and Credibility Issues:Miscollated documents can damage the professionalism and credibility of the sender or organization. It suggests carelessness and a lack of attention to detail, undermining the message being conveyed.
- Increased Costs and Delays:Improper collation can lead to significant costs and delays. Reprints or corrections require additional time and resources, impacting project deadlines and budget.
- Negative Customer Perception:Receiving a miscollated document can create a negative impression on customers or clients. It can reflect poorly on the organization and damage its reputation.
Common Printing Errors Caused by Incorrect Collation
Incorrect collation can lead to various printing errors, ranging from minor inconveniences to major production issues. Here are some common examples:
- Missing Pages:This is a common error caused by improper collation, where certain pages are accidentally omitted from the final document.
- Out-of-Order Pages:This error occurs when pages are not assembled in the correct sequence, leading to a confusing and illogical reading experience.
- Duplicate Pages:In some cases, pages might be duplicated due to incorrect collation, resulting in a longer document than intended.
- Incorrect Binding:If the pages are not collated correctly, the binding process can be affected, leading to uneven or misaligned pages.
Methods of Collation in Printing

Collation is a crucial step in the printing process, ensuring that printed pages are arranged in the correct order before binding. Various methods are employed for collation, ranging from manual techniques to automated systems, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Manual Collation Techniques
Manual collation involves physically arranging printed pages in the correct order. This method is often used for smaller print runs or when dealing with complex projects requiring specific page arrangements.
- Signature Collation:Printed sheets are grouped into “signatures,” which are sets of pages that are printed together and folded. Signatures are then collated in the correct order, creating a complete booklet. This method is commonly used for book printing.
- Sheet-by-Sheet Collation:Each page is individually collated, often using a table or a dedicated collation station. This method is more time-consuming but allows for greater control over the order of pages.
- Hand Collation:This involves manually picking up and placing each page in the correct order, often using a guide or template. Hand collation is suitable for small print runs or projects with unique page arrangements.
Automated Collation Methods
Automated collation utilizes machinery to streamline the collation process, significantly increasing efficiency and accuracy. These methods are commonly used for large print runs or projects requiring high-volume output.
- Gatherer-Stitcher:This machine gathers individual sheets and stitches them together, creating a booklet. The gatherer-stitcher uses a combination of sensors and mechanical arms to ensure accurate collation.
- Perfect Binder:This machine collates and binds pages together using glue. The perfect binder is often used for softcover books and magazines.
- Saddle Stitcher:This machine folds and staples pages together to create a booklet. Saddle stitching is commonly used for brochures, pamphlets, and magazines.
Comparing Manual and Automated Collation
| Feature | Manual Collation | Automated Collation |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slow | Fast |
| Accuracy | Prone to errors | Highly accurate |
| Cost | Low | High (initial investment) |
| Flexibility | High | Limited |
| Labor Requirements | High | Low |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Collation Method
Manual Collation
Advantages:
- Flexibility:Manual collation allows for greater flexibility in page arrangement, making it suitable for projects with unique page sequences.
- Low Cost:Manual collation requires minimal initial investment, making it a cost-effective option for small print runs.
Disadvantages:
- Slow Speed:Manual collation is time-consuming, especially for large print runs.
- Prone to Errors:Human error is a significant factor in manual collation, potentially leading to miscollated pages.
- Labor Intensive:Manual collation requires a significant amount of labor, increasing labor costs.
Automated Collation
Advantages:
- High Speed:Automated collation significantly increases speed and efficiency, especially for large print runs.
- High Accuracy:Automated systems are highly accurate, minimizing the risk of miscollated pages.
- Reduced Labor:Automated collation reduces the need for manual labor, lowering labor costs.
Disadvantages:
- High Initial Investment:Automated collation equipment requires a significant initial investment, making it less cost-effective for small print runs.
- Limited Flexibility:Automated systems may have limited flexibility in page arrangement, making them less suitable for complex projects.
Collation and Binding
Collation and binding are two essential processes in printing that work hand-in-hand to create a finished printed product. Collation refers to the process of arranging printed pages in the correct order, while binding refers to the process of securing the pages together.
The relationship between these two processes is crucial because the chosen binding method often dictates how the pages should be collated.
The Impact of Collation on Binding
The collation method used for a printing project significantly impacts the choice of binding method. For instance, if a document is collated in a signature format, where multiple pages are printed together as a single sheet, then certain binding methods, such as saddle stitching or perfect binding, are more suitable.
Conversely, if the document is collated in a single-sheet format, then other binding methods, such as wire-o binding or spiral binding, might be more appropriate.
Binding Techniques and Their Compatibility with Collation Methods
The following table provides examples of different binding techniques and their compatibility with various collation methods:
| Binding Method | Collation Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Saddle Stitching | Signature | Pages are folded in half and stapled through the fold line. This method is commonly used for magazines, brochures, and booklets. |
| Perfect Binding | Signature | The edges of the pages are glued together to create a smooth spine. This method is often used for books, journals, and paperback novels. |
| Wire-O Binding | Single-Sheet | Pages are punched with holes and bound together with a wire loop. This method is suitable for calendars, notebooks, and reports that need to lay flat. |
| Spiral Binding | Single-Sheet | Pages are punched with holes and bound together with a plastic or metal coil. This method is commonly used for reports, presentations, and documents that need to be easily turned. |
Collation in Digital Printing

Collation in digital printing refers to the process of arranging printed pages in the correct order before binding or finishing. While the concept of collation remains the same across different printing methods, digital printing offers unique advantages and variations in how collation is implemented.
Digital Printing’s Impact on Collation
Digital printing technology simplifies the collation process compared to traditional offset printing. This is because digital printing eliminates the need for separate printing plates for each page, allowing for more flexibility and automation.
- Automated Collation:Digital printing machines often incorporate automated collation systems that automatically arrange pages in the correct order. This reduces the risk of human error and speeds up the printing process.
- On-Demand Printing:Digital printing allows for on-demand printing, meaning that pages can be printed and collated only when needed. This eliminates the need for large print runs and reduces waste.
- Variable Data Printing:Digital printing enables variable data printing, which allows for personalized content on each page. This flexibility in content requires accurate collation to ensure that each printed piece receives the correct information.
Quality Control and Collation
Collation is a crucial step in the printing process, ensuring the correct order of pages within a printed document. But it’s not just about getting the pages in the right sequence; it’s also about maintaining quality throughout the process. Quality control plays a vital role in ensuring that the final printed product is accurate, consistent, and free from errors.
Importance of Quality Control in Collation
Quality control in collation ensures that the printed materials are free from errors and meet the desired standards. This involves verifying the accuracy of the collated pages, checking for any missing or misplaced pages, and identifying any inconsistencies in the printed content.
Effective quality control minimizes the risk of errors, saves time and resources, and ultimately enhances customer satisfaction.
Methods to Ensure Accurate and Consistent Collation
Several methods are used to ensure accurate and consistent collation. These methods can be manual, automated, or a combination of both:
- Visual Inspection:This is a basic method where an operator manually checks each collated set of pages for the correct order. While effective for small batches, it can be time-consuming and prone to human error for larger projects.
- Barcoding and Scanning:This method involves using barcodes or other unique identifiers on each page. These codes are scanned during collation, allowing for automated verification of page order. This method is highly accurate and efficient, especially for large-scale printing projects.
- Collation Machines:Specialized machines are designed for automated collation. These machines use various mechanisms, such as feeders, conveyors, and sensors, to ensure accurate and consistent collation. They are particularly useful for high-volume printing projects.
- Software Solutions:Software solutions are available that can help manage and track the collation process. These solutions often include features for automated page order verification, error detection, and reporting.
Checklist for Verifying the Accuracy of Collated Printed Materials
A checklist can be used to systematically verify the accuracy of collated printed materials. Here is a sample checklist:
- Page Count:Verify that the number of pages in each collated set matches the expected page count for the document.
- Page Order:Check that the pages are in the correct order, starting from the first page and ending with the last page.
- Page Numbering:Ensure that the page numbers are sequential and accurate.
- Binding and Finishing:Verify that the binding and finishing are consistent and meet the specified requirements.
- Print Quality:Inspect the print quality for any defects, such as smudging, misalignment, or color inconsistencies.
- Content Accuracy:Review the content for any errors, omissions, or inconsistencies.
Quick FAQs
What happens if pages are not collated correctly?
Incorrect collation can lead to pages being out of order, missing pages, or even pages being printed in the wrong order. This can make the final product confusing and unusable.
How can I tell if my printed materials have been collated correctly?
The easiest way is to simply flip through the pages and check if they are in the correct order. You can also look for any inconsistencies in page numbering or page layout.
Is collation important for small printing projects?
Yes, even for small projects, collation is important. It ensures that your final product is professional and accurate. Even a single misplaced page can make a big difference.
