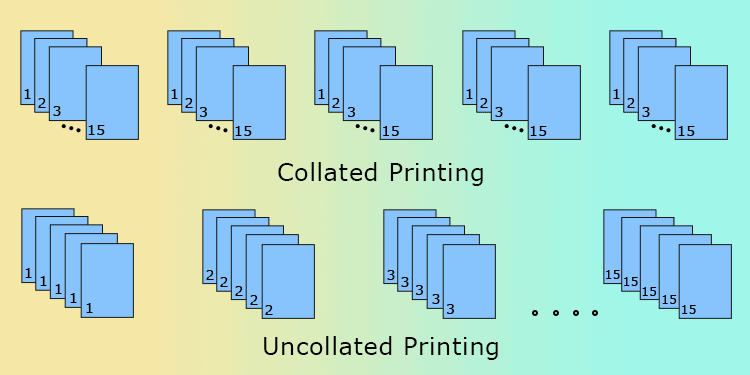
What does collated mean printer – What does collated mean in printing? It’s a term that might sound confusing at first, but it’s actually a fundamental concept in the printing world. Collation refers to the process of arranging printed pages in the correct order, ensuring that your documents, brochures, or books are assembled correctly before they’re bound or finished.
Think of it like assembling a puzzle – each page needs to be in the right spot for the final product to be complete.
Collation is crucial for creating professional-looking printed materials, and it can be done manually, automatically, or digitally. The method used depends on the volume of printing, the complexity of the document, and the desired level of accuracy. We’ll explore the different methods, their advantages and disadvantages, and how collation fits into the larger picture of printing processes and finishing.
Understanding Collation in Printing

Collation is a crucial process in printing that ensures the pages of a document are arranged in the correct order before binding or finishing. This process is essential for maintaining the intended sequence of pages, ensuring the document’s readability and functionality.
The Significance of Collation in Printing
Collation plays a vital role in producing high-quality printed materials. It guarantees that the pages are arranged correctly, preventing errors and ensuring a smooth reading experience.
Examples of Collation in Printing
Collation is used in various printing scenarios, including:
- Book Printing:Collation is crucial for assembling the pages of a book in the correct order. This ensures that the chapters, sections, and pages flow seamlessly, creating a cohesive reading experience.
- Brochure Printing:Collation ensures that the pages of a brochure are arranged in the correct order, allowing the reader to follow the intended message and information flow.
- Document Printing:Collation is essential for organizing documents, ensuring that pages are in the correct order, especially when dealing with multi-page reports, presentations, or manuals.
Benefits of Using Collation in Printing
Collation offers several benefits for printing, including:
- Increased Efficiency:Collation streamlines the printing process, reducing the time and effort required to manually arrange pages. This is particularly beneficial for large printing projects, such as books or brochures.
- Improved Accuracy:Collation ensures that pages are arranged in the correct order, minimizing errors and ensuring the document’s integrity. This is crucial for documents that require accurate information and presentation.
- Enhanced Consistency:Collation guarantees that all copies of a printed document have the same page order, ensuring consistency and professionalism. This is essential for maintaining brand identity and presenting a polished image.
Collation Methods
Collation, the process of arranging printed pages in the correct order, is a crucial step in the printing process. The method of collation employed can significantly impact the efficiency, accuracy, and cost of the printing operation. There are three primary methods of collation: manual, automated, and digital.
Manual Collation
Manual collation involves manually arranging printed pages in the correct order. This method is typically used for small print runs or when high accuracy is not a critical requirement.
- Advantages:Manual collation is cost-effective for small print runs, as it does not require specialized equipment. It also offers flexibility, allowing for easy adjustments to the collation order.
- Disadvantages:Manual collation is time-consuming and prone to errors, especially for larger print runs. The accuracy of manual collation is highly dependent on the operator’s attentiveness and skill.
Automated Collation
Automated collation utilizes specialized equipment to arrange printed pages in the correct order. This method is often employed for medium to large print runs, where speed and accuracy are crucial.
- Advantages:Automated collation is significantly faster and more accurate than manual collation. It reduces the risk of human error and allows for higher throughput.
- Disadvantages:Automated collation requires specialized equipment, which can be a significant investment. It may also be less flexible than manual collation, requiring pre-programmed collation sequences.
Digital Collation
Digital collation is a relatively new method that utilizes digital technology to arrange printed pages in the correct order. This method is typically employed for high-volume print runs, where speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness are paramount.
- Advantages:Digital collation is extremely fast and accurate, eliminating the risk of human error. It also offers significant cost savings compared to traditional methods, as it eliminates the need for manual intervention.
- Disadvantages:Digital collation requires specialized software and equipment, which can be a significant investment. It may also be less flexible than traditional methods, requiring pre-programmed collation sequences.
Collation in Different Printing Processes

Collation is a crucial step in the printing process, ensuring that pages are arranged in the correct order before they are bound or assembled. The way collation is implemented can vary significantly depending on the printing process and the type of printed material.
Collated printing means your printer stacks pages in order, like a magazine. This can be handy for big projects, but if you’re looking for a printer to handle fabric printing, you might want to check out a DTF printer. Wondering how much an Audley DTF printer costs?
You can find out more about pricing here. Of course, whether you choose a collated or DTF printer depends on your specific needs and budget.
Let’s explore how collation is employed in different printing methods.
Collation in Offset Printing
Offset printing, a widely used process for high-volume printing, involves transferring ink from a printing plate to a rubber blanket and then to the final printing surface. In offset printing, collation is typically handled through a combination of manual and automated processes.
- Manual Collation: For smaller print runs, manual collation is common. Printed sheets are stacked and manually arranged in the correct order before being bound.
- Automated Collation: For larger print runs, automated collation systems are used. These systems employ sophisticated machinery that accurately sorts and collates pages at high speeds.
Offset printing often involves printing multiple pages on a single sheet, known as a signature. Collation ensures that these signatures are arranged in the proper sequence before being bound into a finished product.
Collation in Digital Printing
Digital printing offers flexibility and efficiency for smaller print runs and personalized materials. Unlike offset printing, digital printing typically prints one page at a time.
- Inline Collation: Many digital printing presses have inline collation capabilities, where pages are automatically arranged in the correct order as they are printed.
- Offline Collation: For larger digital print jobs, offline collation may be necessary. This involves collecting the printed pages and arranging them manually or using specialized collation equipment.
Digital printing is often used for producing brochures, flyers, and direct mail pieces. Collation ensures that these materials are assembled correctly, delivering a professional and consistent look.
Collation in Large Format Printing
Large format printing, used for producing posters, banners, and other oversized prints, often involves printing on large rolls of material.
- Roll-to-Roll Collation: In roll-to-roll printing, collation is typically handled by the printing equipment itself. The printer automatically aligns and joins the printed rolls in the correct order.
- Panel Collation: For larger projects, panels of printed material may be created and then joined together. Collation ensures that these panels are arranged in the proper sequence.
Large format printing often involves complex designs and layouts. Collation plays a crucial role in ensuring that these designs are accurately assembled, creating visually appealing and impactful displays.
Collation and Print Finishing

Collation is an essential part of the printing process, as it directly influences the efficiency and quality of print finishing operations. Print finishing involves various techniques like binding, folding, and cutting, all of which are impacted by how the printed pages are collated.
Understanding the connection between collation and print finishing is crucial for achieving high-quality, professional-looking printed materials.
Impact of Collation on Print Finishing Efficiency and Quality
Collation significantly impacts the overall efficiency and quality of the print finishing process. When pages are collated correctly, the finishing process becomes streamlined and produces high-quality results. Here’s how:* Streamlined Binding:Accurate collation ensures that pages are in the correct order for binding.
This minimizes the need for manual intervention, reduces errors, and speeds up the binding process.
Consistent Folding
Proper collation ensures that pages are folded correctly, resulting in uniform and consistent folds. This is crucial for projects requiring specific fold patterns, like brochures or leaflets.
Precise Cutting
Collation ensures that pages are aligned accurately for cutting, minimizing the risk of miscuts and ensuring a professional finish.
Influence of Collation Methods on Print Finishing Techniques
Different collation methods influence the choice of print finishing techniques. The choice of collation method is determined by the specific project requirements, such as the number of pages, the type of binding, and the desired finishing quality.* Manual Collation:Manual collation is suitable for smaller projects with fewer pages.
This method can be time-consuming and prone to errors, but it is cost-effective for small-scale printing.
Mechanical Collation
Mechanical collation is more efficient for larger projects with multiple pages. This method uses automated equipment to collate pages accurately and quickly.
Digital Collation
Digital collation is the most efficient method, particularly for high-volume printing. This method uses digital technology to collate pages with exceptional accuracy and speed. Digital collation often facilitates the use of advanced print finishing techniques, such as:* Perfect Binding:This technique uses glue to bind the pages together, creating a smooth, professional finish.
Digital collation allows for precise alignment of pages, ensuring a perfect binding result.
Saddle Stitch Binding
This technique uses staples to bind pages together, suitable for brochures and magazines. Digital collation ensures that pages are accurately aligned for stapling, resulting in a professional finish.
Wire-O Binding
This technique uses wire loops to bind pages together, creating a durable and lay-flat binding. Digital collation ensures that pages are perfectly aligned for wire-o binding, resulting in a professional and high-quality finish.
Troubleshooting Collation Issues
Collation errors can be frustrating, but with a systematic approach, you can identify and resolve them efficiently. Here’s a guide to help you troubleshoot common problems and ensure your printed materials are collated correctly.
Identifying Common Collation Problems
Understanding the common issues that arise during collation is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Here’s a list of typical problems you might encounter:
- Misaligned Pages:Pages might not be aligned properly, leading to uneven margins or pages that are out of place. This can happen due to paper jams, incorrect paper settings, or misaligned feeders.
- Missing Pages:Sometimes, pages might be missing altogether. This can be caused by paper jams, misfeeds, or incorrect page counts during the printing process.
- Incorrect Page Order:The pages might be in the wrong order, resulting in a jumbled document. This can occur due to errors in the printing software, incorrect page numbering, or misconfigured collation settings.
Troubleshooting Techniques
Once you’ve identified a collation problem, you need to determine its cause and implement the appropriate solution. Here are some practical tips to help you troubleshoot:
- Check the Paper Feed:Ensure that the paper is loaded correctly and that there are no jams or misfeeds. Adjust the paper settings to match the paper type and size.
- Review the Collation Settings:Verify that the collation settings in your printing software are correctly configured. Ensure that the correct collation method is selected and that the page order is accurate.
- Inspect the Print Job:Carefully examine the printed pages to identify any misaligned pages, missing pages, or incorrect page order. This will help you pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Check the Printer’s Manual:Refer to your printer’s manual for troubleshooting guides and specific instructions related to collation settings and error messages.
- Perform a Test Print:Run a test print with a small number of pages to verify that the collation settings are working correctly before printing the entire document.
Quality Control Measures
To prevent collation errors and ensure accurate results, implementing quality control measures is essential. Here are some important steps:
- Visual Inspection:Carefully inspect the collated pages for any misaligned pages, missing pages, or incorrect page order. This should be done at each stage of the collation process.
- Page Number Verification:Ensure that the page numbers are sequential and accurate. This can be done by reviewing the page numbers at the bottom or top of each page.
- Random Sampling:Select a random sample of printed documents and check them for collation errors. This helps to identify any systemic issues that may not be apparent in a full inspection.
Collation in a Modern Printing Environment

Gone are the days of manual collation, where stacks of paper were painstakingly sorted and assembled by hand. The modern printing environment has embraced technology to revolutionize the collation process, making it more efficient, accurate, and streamlined.
Automated Collation Systems
Automated collation systems have become an integral part of modern printing operations, significantly enhancing the speed and accuracy of the collation process. These systems use sophisticated technology to automatically gather and assemble pages in the correct order, eliminating the possibility of human error.
Automated collation systems are typically integrated into high-speed printing presses and finishing equipment, ensuring seamless integration with the overall printing workflow.
Digital Printing Technologies
Digital printing technologies have also played a pivotal role in simplifying collation. With digital printing, files are sent directly to the printer, eliminating the need for traditional printing plates and the associated collation challenges. Digital presses often incorporate integrated finishing modules that handle collation, folding, and other finishing processes, further streamlining the workflow.
Software Solutions for Collation
Software solutions have emerged as powerful tools for managing and optimizing the collation process. These software programs provide features such as:
- Pre-flight checks to ensure that files are correctly formatted and ready for printing.
- Automated page numbering and imposition, simplifying the creation of print-ready documents.
- Real-time tracking of collation progress and reporting, allowing for efficient monitoring and troubleshooting.
Digital Workflows and Cloud-Based Printing Services, What does collated mean printer
The rise of digital workflows and cloud-based printing services has further transformed collation practices. Digital workflows enable seamless file sharing and collaboration, simplifying the distribution and management of print jobs. Cloud-based printing services often incorporate automated collation features, ensuring that print jobs are assembled correctly and delivered to the desired location.
Query Resolution: What Does Collated Mean Printer
What are some common collation errors?
Common errors include misaligned pages, missing pages, and incorrect page order. These can occur due to manual handling, equipment malfunctions, or software issues.
How can I prevent collation errors?
Implementing quality control measures, using automated collation systems, and ensuring proper training for operators can help prevent errors.
What are some examples of automated collation systems?
Some examples include high-speed collators, booklet makers, and digital finishing systems.
Is collation necessary for digital printing?
While digital printing often involves automated processes, collation can still be necessary, especially for multi-page documents or projects with specific binding requirements.
