What is a UV printer? It’s a revolutionary printing technology that uses ultraviolet light to cure inks, creating durable and vibrant prints on a wide range of materials. UV printing has revolutionized industries like signage, packaging, and even personalized gifts, offering a unique blend of precision, speed, and lasting quality.
UV printers utilize a process that begins with digital designs being transferred onto specialized UV-curable inks. These inks, formulated to react to UV light, are then applied to the chosen substrate, be it rigid or flexible, through a precise printing mechanism.
The UV lamp, strategically positioned above the printing surface, then emits a burst of ultraviolet radiation. This process instantly cures the inks, solidifying them into a durable, scratch-resistant finish. The result? High-quality, vibrant prints that are resistant to fading, water damage, and abrasion, making them ideal for a wide range of applications.
Introduction to UV Printers
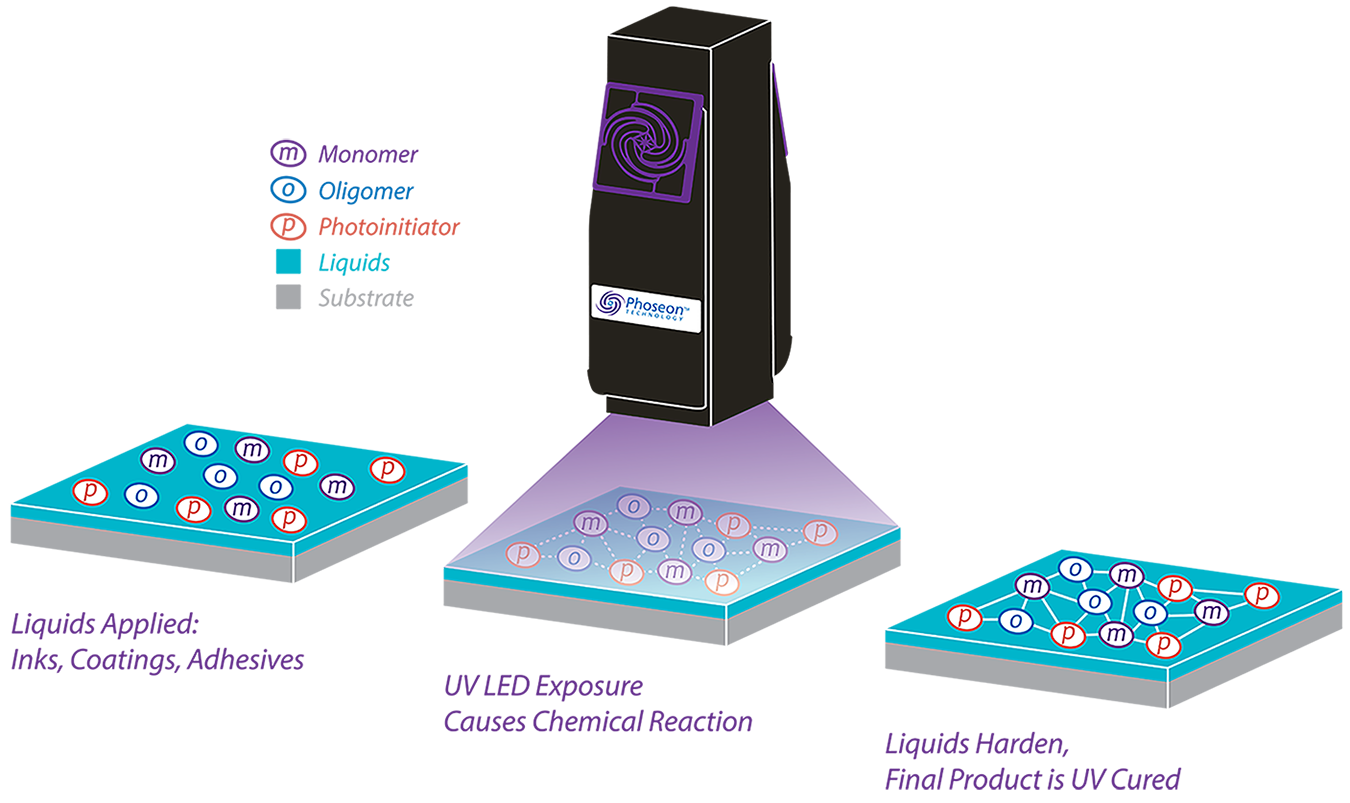
UV printing is a revolutionary technology that has transformed the printing industry, offering a wide range of applications and capabilities. It utilizes ultraviolet (UV) light to cure inks and coatings instantly, enabling faster production and exceptional print quality.
The Science Behind UV Curing
UV curing is a photochemical process that uses UV light to initiate a chemical reaction, causing inks or coatings to solidify rapidly. This process is fundamentally different from traditional printing methods, which rely on heat or solvents to dry the ink.
- UV Light Source:UV printers utilize specialized lamps that emit UV light at specific wavelengths, typically in the range of 200-400 nanometers. This wavelength is absorbed by photoinitiators present in the ink or coating, triggering the curing process.
- Photoinitiators:These are chemical compounds that absorb UV light and initiate the polymerization process. Upon absorbing UV light, photoinitiators generate free radicals, which initiate a chain reaction that causes the ink or coating to solidify.
- Curing Process:As the UV light interacts with the photoinitiators, a series of chemical reactions occur, resulting in the formation of cross-linked polymer chains. This process effectively transforms the liquid ink or coating into a solid, durable finish.
History and Evolution of UV Printing
UV printing technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1970s. Early UV printing systems were primarily used for specialized applications, such as printing on rigid substrates like metal or glass. However, advancements in UV curing technology, coupled with the development of new inks and coatings, have expanded its applications to a wide range of industries.
- Early Development:The first UV printing systems were introduced in the 1970s, primarily for industrial applications. These early systems were bulky and required specialized expertise to operate.
- Advancements in Technology:The 1980s and 1990s witnessed significant advancements in UV curing technology, including the development of more efficient UV lamps and improved inks and coatings. This led to increased adoption of UV printing in various industries.
- Digital UV Printing:The advent of digital printing technology in the late 20th century revolutionized the printing industry. Digital UV printers combine the benefits of UV curing with digital printing capabilities, offering high-resolution, customizable printing on a wide range of substrates.
How UV Printers Work

UV printers are a versatile technology that utilizes ultraviolet (UV) light to cure inks, allowing for high-quality, durable prints on a wide range of materials. The process involves a series of steps, from design creation to the final product.
The Printing Process
The printing process begins with a digital design, typically created using graphic design software. This design is then sent to the UV printer, which uses a specialized printhead to deposit UV ink onto the chosen substrate. The ink is then cured by a UV lamp, which emits ultraviolet light that instantly solidifies the ink, creating a durable, waterproof, and scratch-resistant finish.
UV Inks and Their Properties
UV inks are formulated specifically for use with UV printers and possess unique properties that make them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Rapid Curing:UV inks cure almost instantly upon exposure to UV light, allowing for high-speed printing and immediate handling of the finished product. This rapid curing eliminates the need for lengthy drying times, making UV printing a highly efficient process.
- Durability:UV inks are known for their exceptional durability, offering resistance to scratches, water, and fading. This makes them ideal for applications where longevity and high-quality prints are essential, such as outdoor signage, promotional materials, and industrial parts.
- Versatility:UV inks are available in a wide range of colors, including vibrant hues, metallic finishes, and even clear coatings. This versatility allows for creative designs and finishes on a variety of substrates.
UV Lamps in Printing
UV lamps are an integral part of the UV printing process, responsible for curing the ink and ensuring the print’s durability. Different types of UV lamps are used in UV printing, each with its own advantages and applications.
- Mercury Vapor Lamps:These lamps have been widely used in UV printing for their high output and affordability. However, they contain mercury, a hazardous substance, and have a relatively short lifespan.
- Metal Halide Lamps:These lamps offer higher intensity and efficiency compared to mercury vapor lamps, with a longer lifespan. They also produce a wider spectrum of UV light, making them suitable for curing a wider range of UV inks.
- LED Lamps:LED lamps are becoming increasingly popular in UV printing due to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and low heat output. They are also environmentally friendly, as they do not contain mercury.
Advantages of UV Printing
UV printing offers several advantages over traditional printing methods, making it a popular choice for a wide range of applications. This technology delivers high-quality, durable prints with a faster turnaround time and reduced environmental impact.
Durability and Longevity of UV-Cured Prints
UV-cured inks are known for their exceptional durability and longevity. The UV light instantly dries the ink, creating a robust, scratch-resistant surface that can withstand harsh conditions. This makes UV printing ideal for applications requiring long-lasting prints, such as outdoor signage, vehicle wraps, and industrial labels.
UV-cured inks are highly resistant to fading, scratching, and abrasion, making them ideal for applications where durability is paramount.
Environmental Impact of UV Printing
UV printing offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional printing methods. This technology uses less energy and produces less waste, contributing to a sustainable printing process.
- Reduced energy consumption:UV printing uses less energy compared to traditional methods like screen printing or offset printing, as it doesn’t require heat for drying. This reduces carbon emissions and contributes to a smaller environmental footprint.
- Lower waste production:UV printing generates less waste compared to traditional printing methods. The process involves less material usage and produces fewer chemical byproducts, minimizing environmental impact.
- Eco-friendly inks:Many UV inks are formulated with eco-friendly ingredients and are free of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), reducing air pollution and contributing to a healthier environment.
Applications of UV Printers

UV printing is a versatile technology with applications spanning a wide range of industries, from manufacturing and retail to healthcare and design. This technology has revolutionized the way we create and customize products, offering a wide array of benefits. UV printing allows for the creation of high-quality, durable, and long-lasting prints on a variety of materials.
UV printers are pretty cool, they use UV light to cure the ink, which lets you print on all sorts of materials, even glass! If you’re wondering how to print directly on glass, check out this article: how do you print on glass.
UV printers are great for creating custom designs, logos, or even photos on glass, making them a versatile tool for DIY projects or professional applications.
It’s an eco-friendly printing method, reducing waste and minimizing the use of harmful chemicals. This has made it an increasingly popular choice for businesses seeking sustainable and cost-effective printing solutions.
Applications across Industries
UV printing offers a diverse range of applications across different industries. Here are some examples:
- Manufacturing:UV printing is used to create durable and long-lasting prints on products like electronics, appliances, automotive parts, and industrial equipment. The technology is also used for printing circuit boards, labels, and packaging.
- Retail:UV printing is widely used for creating personalized and customized products, such as phone cases, t-shirts, mugs, and other promotional items. The technology also allows for the creation of high-quality graphics and designs for point-of-sale displays and signage.
- Healthcare:UV printing is used in the healthcare industry to create medical devices, prosthetics, and pharmaceutical packaging. The technology’s ability to print on various materials, including plastics, metals, and glass, makes it suitable for a wide range of medical applications.
- Design and Art:UV printing is used by artists and designers to create high-quality prints on canvas, wood, metal, and other materials. The technology allows for the creation of vibrant and detailed images, making it a popular choice for fine art printing.
Specific Examples of Products and Materials
Here are some specific examples of products and materials suitable for UV printing:
- Phone cases:UV printing allows for the creation of custom phone cases with vibrant and durable designs.
- T-shirts:UV printing is used to create personalized t-shirts with high-quality graphics and designs.
- Mugs:UV printing is used to create personalized mugs with images, text, and logos.
- Signs and banners:UV printing is used to create durable and weather-resistant signs and banners.
- Labels and stickers:UV printing is used to create high-quality labels and stickers for a variety of applications.
- Packaging:UV printing is used to create eye-catching and durable packaging for products of all kinds.
- Automotive parts:UV printing is used to create durable and long-lasting prints on automotive parts, such as dashboards, door panels, and trim pieces.
- Medical devices:UV printing is used to create medical devices, such as prosthetics, implants, and surgical instruments.
- Canvas prints:UV printing is used to create high-quality canvas prints for art and photography.
- Wood prints:UV printing is used to create unique and personalized wood prints for home décor and art.
Growing Use in Niche Markets
UV printing is also gaining popularity in niche markets, such as:
- 3D printing:UV printing is used to create high-resolution and detailed prints for 3D models.
- Personalized medicine:UV printing is used to create customized medical devices and implants, allowing for personalized treatment options.
- Sustainable packaging:UV printing is used to create eco-friendly packaging solutions, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact.
Types of UV Printers
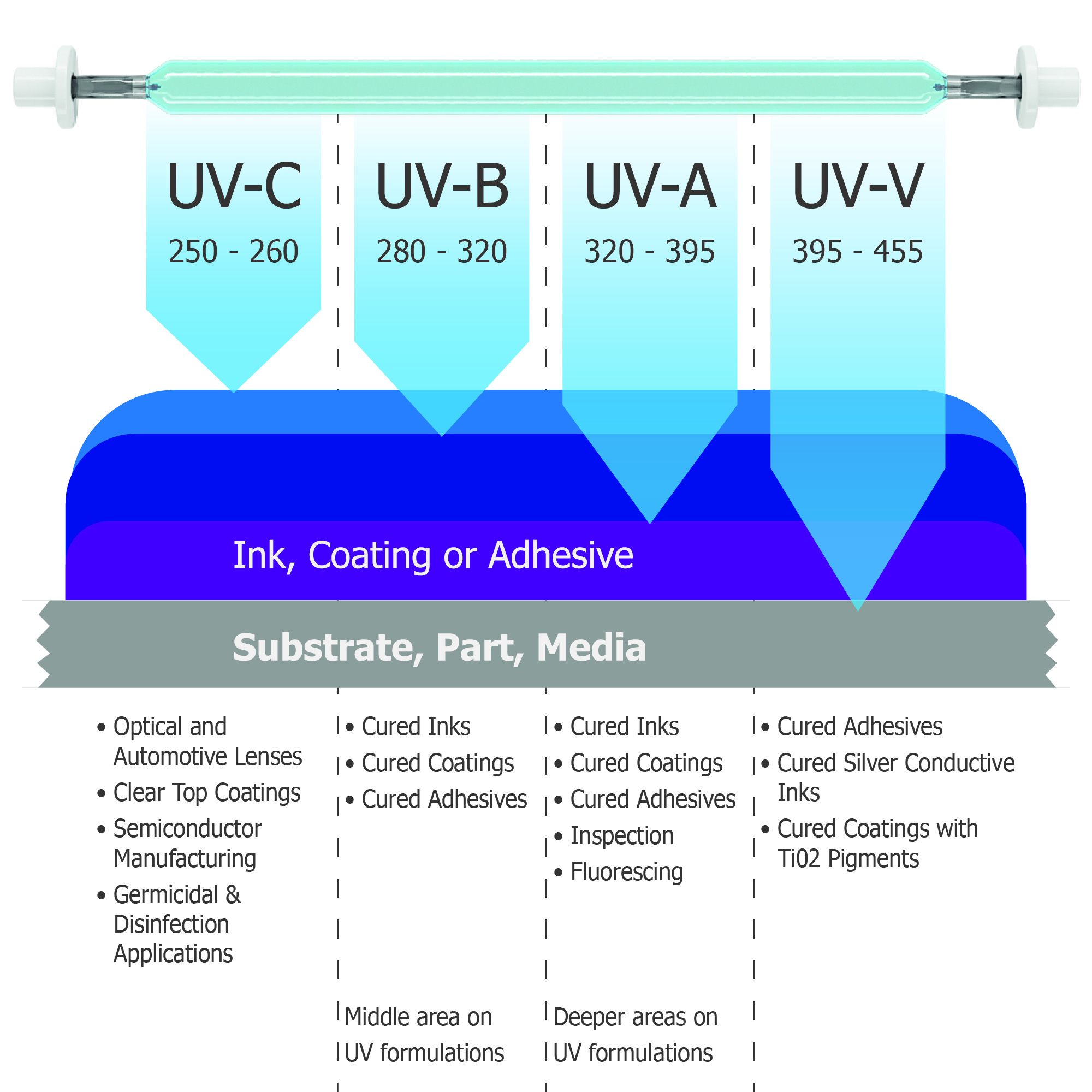
UV printers are categorized based on their technology, functionality, and applications. Understanding these categories is crucial for choosing the right printer for your specific needs. This section explores the different types of UV printers, their features, and their respective strengths and limitations.
UV Flatbed Printers
UV flatbed printers are designed to print directly onto rigid substrates, such as acrylic, wood, glass, metal, and ceramic. They use a flatbed platform that holds the substrate stationary while the printhead moves across it, depositing UV-curable ink in precise patterns.
The key features of UV flatbed printers include:
- High resolution and image quality: They deliver exceptional detail and clarity, making them suitable for high-end applications.
- Versatility in substrate handling: They can accommodate a wide range of substrate thicknesses and sizes.
- Durability and scratch resistance: UV-cured inks are known for their resistance to scratches and abrasion, ensuring long-lasting prints.
However, UV flatbed printers also have limitations:
- Limited printing area: The size of the printing platform restricts the dimensions of the printable substrate.
- Higher initial investment: Flatbed printers are generally more expensive than other types of UV printers.
- Slower printing speeds: Due to the precise movement of the printhead, flatbed printers typically have slower printing speeds compared to roll-to-roll printers.
UV Roll-to-Roll Printers
UV roll-to-roll printers are designed to print on flexible materials, such as vinyl, canvas, paper, and fabric. They utilize a roll-fed system where the substrate is continuously fed through the printer, allowing for high-volume printing. Key features of UV roll-to-roll printers include:
- High-speed printing: Roll-to-roll printers can achieve significantly faster printing speeds compared to flatbed printers.
- Continuous printing: The roll-fed system enables uninterrupted printing for large quantities.
- Cost-effective for high-volume production: The high-speed and continuous printing capabilities make roll-to-roll printers suitable for large-scale production runs.
However, they also have limitations:
- Limited substrate thickness: Roll-to-roll printers are designed for flexible materials and cannot handle thick or rigid substrates.
- Potential for media warping: The continuous feeding process can cause warping or distortion of the substrate, especially with thinner materials.
- Lower resolution compared to flatbed printers: Roll-to-roll printers typically have lower resolution capabilities than flatbed printers.
Hybrid UV Printers
Hybrid UV printers combine the features of both flatbed and roll-to-roll printers, offering greater versatility and flexibility. These printers can handle both rigid and flexible substrates, making them suitable for a wider range of applications. Hybrid UV printers offer the following advantages:
- Versatility in substrate handling: They can print on both rigid and flexible materials.
- High-resolution printing: Hybrid printers typically achieve higher resolution compared to roll-to-roll printers.
- Faster printing speeds: They offer faster printing speeds compared to flatbed printers, especially for large-format printing.
However, they also have limitations:
- Higher initial investment: Hybrid printers are generally more expensive than dedicated flatbed or roll-to-roll printers.
- More complex operation: The combination of flatbed and roll-to-roll functionalities can make operation more complex.
Direct-to-Garment (DTG) UV Printers, What is a uv printer
Direct-to-garment (DTG) UV printers are specifically designed for printing directly onto textiles, such as t-shirts, hoodies, and other garments. They use a specialized printhead that deposits UV-curable ink directly onto the fabric. Key features of DTG UV printers include:
- High-quality prints on garments: They produce vibrant and detailed prints that are durable and washable.
- Versatility in garment types: DTG printers can handle a wide range of fabric types and colors.
- Cost-effective for small-scale garment printing: DTG printers are a cost-effective option for printing small batches of garments.
However, DTG UV printers also have limitations:
- Limited print area: The size of the printhead restricts the printing area on garments.
- Pre-treatment required: Garments often need to be pre-treated with a special solution to ensure proper ink adhesion.
- Slower printing speeds: DTG printers typically have slower printing speeds compared to other types of UV printers.
Table of Key Characteristics of Popular UV Printer Models
| Printer Model | Type | Technology | Resolution | Print Area | Applications ||—|—|—|—|—|—|| Roland VersaUV LEF-20 | Flatbed | UV-LED | 1440 dpi | 16.9″ x 12.6″ | Prototyping, signage, personalized products || Mimaki UJF-3042 MkII | Flatbed | UV-LED | 1200 dpi | 12.6″ x 19.7″ | Industrial printing, packaging, electronics || Canon imagePROGRAF PRO-4000 | Roll-to-roll | UV-LED | 4800 dpi | 17″ x 24″ | Fine art printing, photography, graphic arts || HP Latex 360 | Roll-to-roll | Latex | 1200 dpi | 54″ | Outdoor signage, banners, vehicle wraps || Kornit Avalanche | DTG | UV-LED | 1200 dpi | 16″ x 20″ | Garment printing, apparel customization |
Choosing the Right UV Printer
Selecting the ideal UV printer for your specific needs involves careful consideration of various factors. To make an informed decision, you should evaluate your printing requirements, budget, and the features offered by different UV printer models.
Evaluating Printer Specifications and Features
A comprehensive checklist helps in assessing the suitability of a UV printer for your applications. Here are some key aspects to evaluate:
- Print Resolution:The resolution of a UV printer determines the level of detail and sharpness in the printed output. Higher resolutions result in sharper images and finer details, making them suitable for high-quality graphics, photos, and intricate designs.
- Print Size:The print size refers to the maximum area that a UV printer can print. Consider the dimensions of the materials you plan to print on and choose a printer with a print size that accommodates your requirements.
- Print Speed:The print speed indicates the time taken to print a specific area. Faster print speeds are beneficial for high-volume printing operations, while slower speeds may be suitable for projects requiring intricate details or precise color matching.
- Print Quality:The quality of the printed output depends on various factors, including the resolution, ink type, and printer technology. Evaluate the printer’s color accuracy, image sharpness, and overall print quality to ensure it meets your standards.
- Ink Type:UV printers utilize specialized inks that cure under UV light. The type of ink determines the durability, color gamut, and overall performance of the print. Consider the application and substrate compatibility when choosing an ink type.
- Substrate Compatibility:UV printers can print on a wide range of materials, including plastics, glass, metal, and wood. Ensure the printer is compatible with the substrates you plan to use.
- Durability:The durability of the printed output is crucial for applications where the printed materials will be exposed to harsh conditions. Choose a printer with inks that offer excellent resistance to fading, scratches, and abrasion.
- Maintenance Requirements:UV printers require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Consider the complexity and frequency of maintenance tasks before purchasing a printer.
- Cost of Operation:The cost of operation includes ink consumption, maintenance, and energy consumption. Evaluate the overall cost of running the printer to determine its economic viability.
- Warranty and Support:A reliable warranty and comprehensive support services are essential for ensuring long-term performance and peace of mind.
Determining Optimal Print Resolution and Print Size
The optimal print resolution and print size depend on the specific application and desired output quality.
- High-resolution printingis generally recommended for applications requiring intricate details, fine lines, and sharp images. For example, printing high-quality photographs, artwork, or product packaging.
- Lower resolution printingmay be sufficient for applications where detailed images are not essential, such as printing signage, promotional materials, or basic graphics.
- Print sizeshould be determined by the dimensions of the materials being printed. For instance, printing on small items like keychains or phone cases requires a smaller print size, while printing large banners or billboards requires a larger print size.
UV Printing: The Future

The realm of UV printing is continuously evolving, with advancements in technology pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. From enhanced print quality and speed to innovative applications, the future of UV printing holds exciting possibilities for various industries.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
UV printing technology is constantly evolving, with several emerging trends shaping its future.
- Increased Automation:UV printers are becoming more automated, with features like automated substrate handling and ink management. This reduces manual intervention, leading to increased efficiency and reduced production costs.
- Advanced Materials:The use of UV-curable inks is expanding to include new materials like flexible plastics, glass, and even metals. This opens up new avenues for UV printing applications, such as 3D printing and industrial coatings.
- Enhanced Print Quality:UV printing technology is continuously improving, offering higher resolutions, sharper detail, and wider color gamuts. This allows for the creation of more intricate and visually appealing prints.
- Sustainable Practices:UV printing is becoming more eco-friendly, with the development of low-VOC inks and energy-efficient printers. This aligns with the growing demand for sustainable printing solutions.
Potential Future Applications
UV printing’s versatility and capabilities are driving its adoption across diverse industries. Here are some potential future applications:
- Personalized Medicine:UV printing could play a crucial role in personalized medicine, enabling the creation of customized medical devices and implants. For example, UV printing can be used to create 3D-printed medical models for surgical planning or personalized drug delivery systems.
- Smart Packaging:UV printing can be used to create smart packaging with embedded sensors and electronics. This allows for real-time monitoring of product conditions, such as temperature and humidity, enhancing product safety and traceability.
- Textile and Fashion:UV printing is revolutionizing the textile and fashion industry, enabling the creation of unique and intricate designs on fabrics. This allows for greater customization and personalization in clothing and accessories.
- Automotive Industry:UV printing is gaining traction in the automotive industry for creating custom decals, interior trims, and even functional parts. Its durability and high-quality finish make it an ideal solution for automotive applications.
Impact on Industries
UV printing is expected to have a significant impact on various industries in the coming years:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity:Automation and faster printing speeds will lead to increased efficiency and productivity in various industries, reducing production times and costs.
- Enhanced Product Customization:UV printing enables greater customization and personalization of products, allowing businesses to cater to specific customer needs and preferences.
- New Product Development:The ability to print on a wider range of materials opens up new possibilities for product development and innovation, leading to the creation of unique and functional products.
- Sustainable Practices:The adoption of eco-friendly UV printing technologies will contribute to sustainable practices across industries, reducing environmental impact and promoting responsible manufacturing.
Clarifying Questions: What Is A Uv Printer
What are the common materials used in UV printing?
UV printing can be applied to a wide variety of materials, including plastics, glass, metal, wood, ceramics, and even textiles.
What are the limitations of UV printing?
While UV printing offers numerous advantages, it does have limitations. One notable limitation is the potential for color discrepancies, especially when printing large quantities. It’s crucial to calibrate the printer regularly to ensure consistent color accuracy.
Is UV printing environmentally friendly?
UV printing is considered more environmentally friendly than traditional printing methods due to its reduced solvent usage and faster curing process. However, it’s essential to choose UV inks that are formulated with eco-friendly ingredients.
