What is collated printing? Imagine you’re creating a booklet or a stack of documents, and you need each page to be in the correct order. Collated printing is the process of ensuring that printed pages are arranged in the right sequence, making it easy for you to assemble and bind them into a final product.
Whether you’re printing brochures, reports, or even textbooks, collated printing guarantees a professional and user-friendly result.
Think about the last time you picked up a magazine or a brochure. Did you notice that the pages were in the right order? That’s thanks to collated printing! It’s a fundamental part of the printing process that ensures the pages are assembled correctly, creating a cohesive and easy-to-follow document.
What is Collated Printing?
Collated printing is a printing method where pages are printed in the correct order and grouped together to form complete sets of documents. This is the most common method of printing for documents that contain multiple pages, such as books, magazines, brochures, and reports.
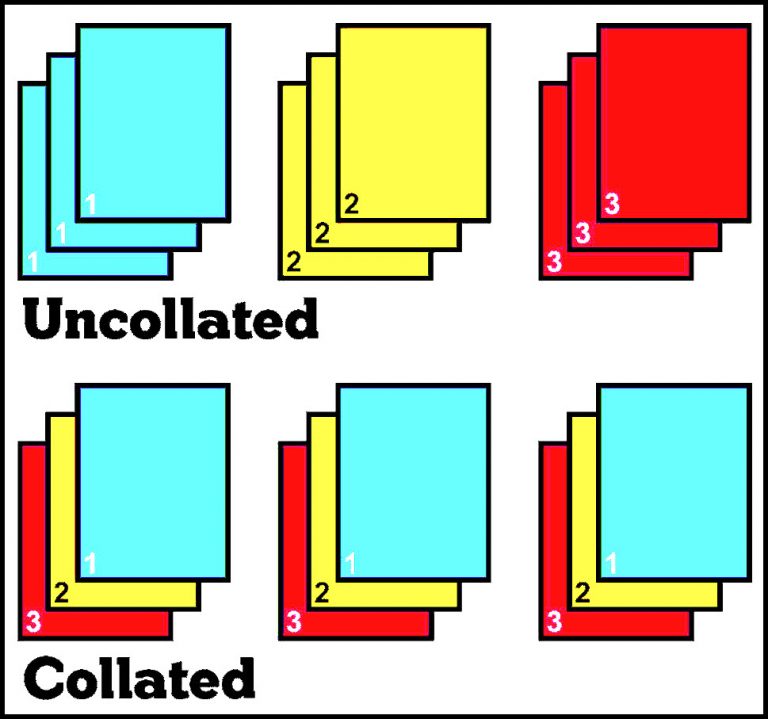
Collated vs. Uncollated Printing
Collated printing ensures that the pages of a document are printed in the correct order and assembled into complete sets. In contrast, uncollated printing prints all pages of a document in a single run, regardless of their order. This means that the pages need to be manually sorted and assembled after printing.
Real-World Examples of Collated Printing
Collated printing is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Books and Magazines: When you purchase a book or magazine, you expect the pages to be in the correct order. This is because the pages were printed using collated printing.
- Brochures and Flyers: These marketing materials often have multiple pages that need to be printed in a specific order. Collated printing ensures that the pages are assembled correctly so that the information flows seamlessly.
- Reports and Presentations: When you print a report or presentation, you want the pages to be in the right order. Collated printing guarantees that the information is presented in a logical and organized manner.
- Invoices and Statements: These documents often contain multiple pages with important information. Collated printing ensures that all pages are present and in the correct order for accurate record-keeping.
How Collated Printing Works
Collated printing ensures that printed pages are arranged in the correct order, ready for binding or other finishing processes. This process involves gathering individual sheets of printed material and assembling them into sets, with each set containing all the pages in the intended sequence.
Manual Collation
Manual collation is the traditional method of arranging printed pages by hand. It involves carefully placing each page in its correct position within a set.
- Process:The process begins with sorting the printed pages into stacks based on their page numbers. The operator then takes one page from each stack, forming a complete set. This process is repeated until all pages are collated.
- Advantages:Manual collation is simple, cost-effective, and requires minimal equipment. It’s suitable for small-scale printing projects where the volume of pages is manageable.
- Disadvantages:It’s time-consuming, prone to errors, and can be tedious, especially for large projects. The risk of misplacing or misordering pages increases with larger print runs.
Mechanical Collation
Mechanical collation utilizes specialized equipment to automate the process of arranging printed pages. This method offers significant advantages in terms of speed, accuracy, and efficiency.
- Process:Mechanical collators use a series of feeders and conveyors to gather pages from different stacks. They then assemble the pages into sets, based on programmed instructions. The collated sets are often stacked or bundled for further processing.
- Advantages:Mechanical collation is faster, more accurate, and can handle large volumes of pages. It reduces the risk of errors and increases productivity.
- Disadvantages:Mechanical collators can be expensive to purchase and maintain. They require specialized training for operation and may not be suitable for very small print runs.
Digital Collation
Digital collation is a modern method that leverages digital printing technologies to ensure accurate page sequencing. This method eliminates the need for physical sorting and assembling of pages.
- Process:Digital collators typically use software to manage and arrange the printed pages electronically. The print driver or software automatically generates the correct page order for printing. The printed output is delivered in the intended sequence, eliminating the need for manual collation.
- Advantages:Digital collation is highly accurate, eliminates manual labor, and offers flexibility in page order and layout. It’s ideal for projects with complex page arrangements or variable data.
- Disadvantages:Digital collation requires specialized printing equipment and software, which can be expensive. It may not be suitable for all printing projects, particularly those with very specific requirements or legacy printing systems.
Benefits of Collated Printing

Collated printing offers a range of advantages that can significantly benefit businesses and individuals alike. It simplifies the process of assembling printed materials, improves efficiency, and enhances the overall presentation and usability of documents.Collated printing is particularly advantageous when dealing with large volumes of printed materials, such as brochures, reports, or manuals.
It ensures that pages are arranged in the correct order, eliminating the need for manual sorting and assembly. This not only saves time and effort but also minimizes the risk of errors.
Improved Efficiency and Reduced Costs
Collated printing streamlines the printing process, reducing the time and effort required to assemble documents. This can lead to significant cost savings, particularly for businesses that print large quantities of materials.
Collated printing is like magic for multi-page documents. It makes sure your pages are in the right order, so you don’t have to spend time shuffling them yourself. But what about finding the right drivers for your printer on Linux?
You can find out if Linux allows downloading printer drivers here. Once you’ve got those drivers, collated printing is just a click away, making your printing experience much smoother.
- Reduced labor costs:Collated printing eliminates the need for manual sorting and assembly, which can significantly reduce labor costs, especially for large print runs.
- Increased productivity:By automating the collation process, collated printing allows businesses to print and assemble documents faster, increasing overall productivity.
- Minimized errors:Collated printing ensures that pages are arranged in the correct order, minimizing the risk of errors that can occur during manual assembly.
Enhanced Presentation and Usability
Collated printing plays a crucial role in enhancing the presentation and usability of printed materials. It ensures that documents are assembled professionally, creating a positive impression on recipients.
- Professional appearance:Collated documents have a professional and polished look, reflecting positively on the sender or organization.
- Improved readability:Collated documents are easy to read and navigate, as pages are arranged in the correct order, enhancing the overall user experience.
- Enhanced brand image:By presenting professionally printed and collated materials, businesses can strengthen their brand image and project a sense of professionalism and reliability.
Specific Situations Where Collated Printing is Advantageous
Collated printing is particularly advantageous in specific situations, such as:
- Large print runs:For businesses that print large quantities of documents, such as brochures, reports, or manuals, collated printing can significantly reduce the time and effort required for assembly.
- Multi-page documents:Collated printing is essential for assembling multi-page documents, ensuring that pages are arranged in the correct order.
- High-volume printing:Businesses that engage in high-volume printing, such as printing companies or document management services, can benefit from the efficiency and cost savings offered by collated printing.
- Marketing materials:Collated printing is widely used for producing marketing materials, such as brochures, flyers, and catalogs, ensuring that these materials are presented professionally and effectively.
Collated Printing in Different Industries
Collated printing finds its niche in a diverse range of industries, each with unique requirements and applications. From the world of publishing to the dynamic realm of marketing and the structured environment of education, collated printing plays a crucial role in delivering high-quality printed materials.
Publishing
Collated printing is a cornerstone of the publishing industry, ensuring the efficient production of books, magazines, and other printed materials. The process is particularly vital for producing large print runs, where accuracy and speed are paramount.Collated printing is essential for creating multi-page documents in the correct order.
In book publishing, for instance, collated printing ensures that pages are assembled in the right sequence, resulting in a seamless reading experience. This is crucial for maintaining the flow of the narrative and ensuring that readers are not confronted with disjointed content.
Marketing
Collated printing is a powerful tool in the marketing world, enabling businesses to create impactful marketing materials that reach their target audience effectively. Brochures, flyers, and other promotional materials are often printed in collated format to ensure that each piece contains the desired information and visual elements.Collated printing helps marketers produce high-quality materials that enhance brand identity and convey a professional image.
For example, a company launching a new product might use collated printing to create brochures that highlight the product’s features and benefits, showcasing the brand’s commitment to quality and detail.
Education
Collated printing is indispensable in the education sector, facilitating the creation of educational materials such as textbooks, workbooks, and handouts. Its accuracy and efficiency are vital for producing large quantities of these materials, ensuring that students have access to the resources they need.Collated printing ensures that educational materials are produced with precision, maintaining the integrity of the content and fostering a positive learning experience.
For example, a university might use collated printing to produce textbooks that include complex diagrams, charts, and tables, ensuring that students receive the necessary visual aids for understanding complex concepts.
Types of Collated Printing
Collated printing can be achieved using a variety of printing methods, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right method depends on factors such as project size, budget, and desired quality. Here’s a look at some common types of collated printing:
Offset Printing
Offset printing is a traditional and widely used method that offers high-quality results at a relatively low cost per unit, especially for large print runs. It uses an offset printing press, which transfers ink from a plate to a rubber blanket and then to the paper.
- High-quality results:Offset printing produces sharp, vibrant images and crisp text, making it ideal for projects that require a professional finish.
- Cost-effective for large runs:The initial setup costs for offset printing are higher than for digital printing, but the cost per unit decreases significantly as the print run increases. This makes it an economical choice for projects with large print volumes.
- Versatile:Offset printing can be used to print a wide range of materials, including paper, cardstock, and even some plastics.
Offset printing is suitable for projects like magazines, brochures, books, and business cards, where large quantities are needed.
Digital Printing
Digital printing is a more modern method that uses digital files to print directly onto paper. This method eliminates the need for plates and allows for quick turnaround times, making it ideal for short-run projects and personalized printing.
- Quick turnaround times:Digital printing can produce printed materials within hours, making it a good option for urgent projects or when quick revisions are needed.
- Cost-effective for short runs:Digital printing is more cost-effective than offset printing for smaller print runs, as there are no plate costs involved.
- Variable data printing:Digital printing allows for variable data printing, which enables you to personalize each printed piece with unique information, such as names, addresses, or promotional offers.
Digital printing is ideal for projects like business cards, flyers, brochures, and direct mail pieces, where smaller quantities or personalized printing is required.
Large-Format Printing
Large-format printing uses specialized printers to produce high-quality prints on large-scale materials like banners, posters, and signage. It is a versatile method that can be used for both indoor and outdoor applications.
- High-resolution prints:Large-format printers can produce high-resolution prints, ensuring sharp images and clear text even at large sizes.
- Wide range of materials:Large-format printing can be used to print on various materials, including vinyl, canvas, paper, and even fabric.
- Durable prints:Large-format prints are designed to be durable and weather-resistant, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor use.
Large-format printing is ideal for projects like trade show displays, event signage, outdoor advertising, and architectural blueprints.
Choosing the Right Type of Collated Printing
The best type of collated printing for a particular project depends on a number of factors, including:
- Print volume:Offset printing is more cost-effective for large print runs, while digital printing is better for smaller runs.
- Budget:Offset printing can be more expensive upfront but offers lower costs per unit for large runs. Digital printing is more affordable for smaller runs.
- Turnaround time:Digital printing offers faster turnaround times than offset printing.
- Quality requirements:Offset printing typically produces higher-quality prints than digital printing, but both methods can deliver professional results.
- Customization needs:Digital printing allows for variable data printing, enabling personalized pieces. Offset printing is less flexible in this regard.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the type of collated printing that best suits your needs and budget.
Collated Printing vs. Uncollated Printing

Collated and uncollated printing are two different methods of printing that affect how pages are arranged and assembled. Understanding the differences between these methods is crucial for making informed decisions about your printing projects. This section will delve into the key features, advantages, and disadvantages of each method, and explore the factors that influence the choice between them.
Comparison of Collated and Uncollated Printing
The following table summarizes the key features, advantages, and disadvantages of collated and uncollated printing:
| Feature | Collated Printing | Uncollated Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Page Order | Pages are printed in the correct sequence and assembled into complete sets. | Pages are printed in a single run, with all copies of each page printed consecutively. |
| Assembly | Pages are assembled into complete sets during the printing process. | Sets must be assembled manually after printing. |
| Efficiency | More efficient for large print runs. | Less efficient for large print runs. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive than uncollated printing. | Generally less expensive than collated printing. |
| Accuracy | Less prone to errors in page order. | More prone to errors in page order. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible for printing different versions of a document. | More flexible for printing different versions of a document. |
Factors Influencing the Choice
Several factors influence the decision to use collated or uncollated printing:
- Print Run Size:Collated printing is more efficient for large print runs, as it reduces the time and effort required for manual assembly. Uncollated printing is more suitable for small print runs where manual assembly is manageable.
- Budget:Collated printing is generally more expensive than uncollated printing due to the added complexity of the printing process. If budget is a major concern, uncollated printing may be a more cost-effective option.
- Accuracy Requirements:Collated printing ensures accurate page order, reducing the risk of errors. Uncollated printing requires manual assembly, which can introduce errors in page order, especially for large print runs.
- Flexibility:Uncollated printing offers more flexibility for printing different versions of a document, as each page can be printed separately. Collated printing is less flexible in this regard, as all pages are printed in a single run.
Scenarios for Collated and Uncollated Printing
Here are some examples of scenarios where each method is most suitable:
- Collated Printing:
- Large-scale marketing materials:Collated printing is ideal for printing large quantities of brochures, flyers, or other marketing materials that need to be assembled into complete sets for distribution.
- Books and magazines:Collated printing is used for printing books and magazines, ensuring accurate page order and efficient assembly.
- Financial reports and legal documents:Collated printing is essential for printing financial reports and legal documents that require accurate page order and consistent formatting.
- Uncollated Printing:
- Small-scale projects:Uncollated printing is suitable for small-scale projects, such as printing personal documents, flyers for a local event, or short-run promotional materials.
- Multiple versions of a document:Uncollated printing is ideal for printing multiple versions of a document, as each page can be printed separately and then assembled into different sets.
- Projects with limited budget:Uncollated printing can be a cost-effective option for projects with limited budgets, as it eliminates the added cost of collated printing.
Tips for Effective Collated Printing
Collated printing is a versatile and efficient printing method, but to achieve the best results, it’s crucial to follow some key tips and best practices. This section will guide you through the process of selecting the right materials, ensuring quality control, and implementing strategies for optimal output.
Choosing the Right Paper Stock, What is collated printing
The paper stock you choose plays a significant role in the overall quality and aesthetic appeal of your collated print project. Consider the following factors when selecting paper:
- Weight:The weight of the paper, measured in grams per square meter (gsm), determines its thickness and durability. Heavier paper stocks are more substantial and suitable for projects that require a premium feel, while lighter stocks are more economical for everyday use.
- Finish:Paper finishes range from smooth to textured, each contributing to the visual and tactile experience of the printed material. Glossy finishes provide a sleek, high-quality look, while matte finishes offer a more subtle and professional appearance.
- Color:While white paper is the most common choice, consider using colored paper to enhance the visual impact of your project. For example, using a light cream or off-white paper can create a vintage aesthetic, while vibrant colors can add a touch of energy and excitement.
Ink Selection and Considerations
Ink selection is critical for ensuring vibrant colors, crisp lines, and long-lasting print quality.
- Type of Ink:There are two main types of ink used in printing: dye-based and pigment-based. Dye-based inks are typically less expensive but can fade over time, especially when exposed to sunlight. Pigment-based inks are more durable and resistant to fading, making them a better choice for projects that require long-lasting color.
- Color Gamut:The color gamut refers to the range of colors that a particular ink can reproduce. A wider color gamut allows for more vibrant and accurate color reproduction. Consider using inks with a wide color gamut for projects that require high-quality color accuracy, such as photography or fine art prints.
- Drying Time:The drying time of ink can impact the speed of the printing process and the potential for smudging. Quick-drying inks are ideal for high-volume printing, while slower-drying inks may be necessary for certain types of paper or finishing techniques.
Finishing Options and Their Impact
Finishing options add a professional touch to your collated print projects and can enhance their functionality.
- Binding:Binding methods, such as stapling, coil binding, or perfect binding, secure the pages together and give the printed material a finished look. The choice of binding method depends on the project’s size, budget, and desired aesthetic.
- Folding:Folding can be used to create brochures, leaflets, or other multi-page documents. The type of fold (e.g., tri-fold, letter fold) depends on the desired layout and design.
- Lamination:Lamination adds a protective layer to printed materials, making them more durable and resistant to wear and tear. It also enhances the visual appeal of the printed material by adding a glossy or matte finish.
Quality Control and Proofreading
Quality control is essential for ensuring that your collated print projects meet your expectations.
- Proofreading:Thorough proofreading is crucial for catching any errors in text, grammar, or layout before the final print run. Consider having multiple people proofread the document to ensure that all errors are identified.
- Color Calibration:Accurate color calibration is essential for ensuring that the colors in your printed materials match your digital designs. Use a color calibration tool to ensure that your monitor is displaying colors accurately.
- Pre-Flight Checks:Before sending your files to the printer, perform pre-flight checks to ensure that the files are in the correct format, have the appropriate resolution, and do not contain any errors. This will help to avoid any printing problems or delays.
FAQ Corner
What is the difference between collated and uncollated printing?
Collated printing arranges pages in the correct order, while uncollated printing prints pages in a single stack, requiring manual sorting.
How does collated printing benefit businesses?
Collated printing helps businesses create professional-looking documents, improve efficiency, and save time by eliminating the need for manual sorting.
What are some common applications of collated printing?
Collated printing is used for a wide range of materials, including brochures, magazines, reports, textbooks, and marketing materials.
What factors should I consider when choosing a collated printing method?
Consider your budget, the volume of printing, the type of document, and the desired finish when selecting a collated printing method.
